Page 29 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 29
El‑Sheimy and Li Satell Navig (2021) 2:7 Page 19 of 23
Table 12 Future trends of PLAN sensors
Sensor Future trend
HD map Reduced maintenance cost (e.g., through crowdsourcing)
Improved update frequency
LiDAR Lower cost and smaller size
Longer range
Camera Improved physical performance (e.g., self‑cleaning, improved dynamic
range, stronger low‑light sensitivity, and stronger near‑infrared
sensitivity)
RADAR Reduced cost
Improved measurement density
WiFi/BLE Longer range, lower power consumption
New range and direction measurements
5G Denser and more miniaturized base station
Multipath‑assisted localization; cooperative localization
New range and direction measurements
LPWAN Higher base station density
New range and direction measurements
INS Lower sensor errors
GNSS Multi‑frequency and multi‑system
Smaller size and power consumption
UWB/Ultrasonic Reduced cost
Longer range of low‑cost systems
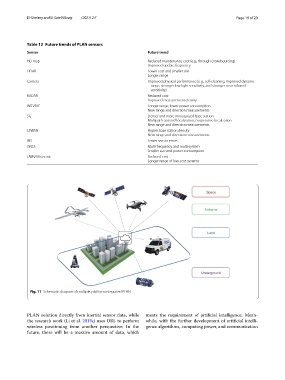
Fig. 11 Schematic diagram of multiple‑platform integrated PLAN
PLAN solution directly from inertial sensor data, while meets the requirement of artifcial intelligence. Mean-
the research work (Li et al. 2019c) uses DRL to perform while, with the further development of artifcial intelli-
wireless positioning from another perspective. In the gence algorithms, computing power, and communication
future, there will be a massive amount of data, which