Page 196 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 196
Li et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:1 Page 10 of 14
coordinate) with the ground truth (ECEF coordinate)
using a rigid body transformation (Horn 1987) and calcu-
lated the position diferences of each matched positions.
Te RMS of position diferences of S-VINS in the local
coordinate system is given in Table 5.
Positioning capacity of the S‑VINS aided multi‑GNSS PPP
solution
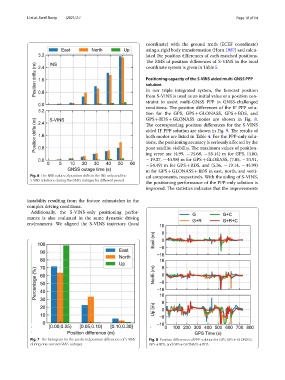
In our triple integrated system, the forecast position
from S-VINS is used as an initial value or a position con-
straint to assist multi-GNSS PPP in GNSS-challenged
conditions. Te position diferences of the IF PPP solu-
tion for the GPS, GPS + GLONASS, GPS + BDS, and
GPS + BDS + GLONASS modes are shown in Fig. 8.
Te corresponding position diferences for the S-VINS
aided IF PPP solution are shown in Fig. 9. Te results of
both modes are listed in Table 4. For the PPP-only solu-
tions, the positioning accuracy is seriously afected by the
poor satellite visibility. Te maximum values of position-
ing error are (4.99, − 24.68, − 55.14) m for GPS, (4.80,
− 19.37, − 44.98) m for GPS + GLOBASS, (7.05, − 24.91,
− 54.49) m for GPS + BDS, and (5.36, − 19.14, − 44.99)
m for GPS + GLONASS + BDS in east, north, and verti-
Fig. 6 The RMS values of position drifts in the INS-only and the cal components, respectively. With the aiding of S-VINS,
S-VINS solutions during the GNSS outages for diferent period
the positioning performance of the PPP-only solution is
improved. Te statistics indicates that the improvements
instability resulting from the feature mismatches in the
complex driving conditions.
Additionally, the S-VINS-only positioning perfor-
mance is also evaluated in the same dynamic driving
environment. We aligned the S-VINS trajectory (local
Fig. 7 The histogram for the predicted position diferences of S-VINS Fig. 8 Position diferences of PPP solution for GPS, GPS + GLONASS,
during one-second GNSS outages GPS + BDS, and GPS + GLONASS + BDS