Page 197 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 197
Li et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:1 Page 11 of 14
a signifcant improvement with the aiding of S-VINS in
such GNSS-challenged conditions. Te main contribu-
tion of S-VINS is to provide a high-accuracy forecast
position, which is immune to the unexpected sudden
changes in the observation environment such as short-
term GNSS signal losses. However, the absolute posi-
tioning accuracy of the S-VINS aided PPP solution still
depends on the precision of PPP.
Positioning performance of the triple integrated system
Te positioning performance of the triple integrated
system is evaluated in this section. For comparison, the
multi-GNSS PPP/INS solutions are calculated and ana-
lyzed. Te combined mode of GPS + GLONASS + BDS
is applied in the IF PPP processing. Te position difer-
ences of the multi-GNSS PPP/S-VINS, LC multi-GNSS
PPP/INS, and TC multi-GNSS PPP/INS are shown in
Fig. 10, and the corresponding RMSs are listed in Table 5.
As expected, the positioning accuracy of the multi-GNSS
PPP/S-VINS solution is further improved by the S-VINS
augmentation. Te results show that the position RMS
of the multi-GNSS PPP/S-VINS solution is 0.88, 1.47,
and 0.96 m with an improvement of 7.4%, 6.4%, and
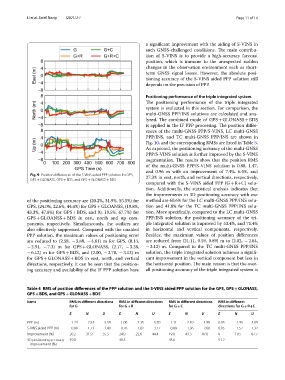
Fig. 9 Position diferences of the S-VINS aided PPP solution for GPS, 27.3% in east, north, and vertical directions, respectively,
GPS + GLONASS, GPS + BDS, and GPS + GLONASS + BDS
compared with the S-VINS aided PPP (G + R+C) solu-
tion. Additionally, the statistical analysis indicates that
the improvements in 3D positioning accuracy with our
of the positioning accuracy are (20.2%, 31.9%, 55.5%) for method are 60.6% for the LC multi-GNSS PPP/INS solu-
GPS, (24.0%, 22.6%, 44.4%) for GPS + GLOANSS, (19.8%, tion and 41.8% for the TC multi-GNSS PPP/INS solu-
43.3%, 47.8%) for GPS + BDS, and (0, 19.5%, 67.7%) for tion. More specifcally, compared to the LC multi-GNSS
GPS + GLOANSS + BDS in east, north and up com- PPP/INS solution, the positioning accuracy of the tri-
ponents, respectively. Simultaneously, the outliers are ple integrated solution is improved by 53.4%, and 71.4%
also efectively suppressed. Compared with the unaided in horizontal and vertical components, respectively.
PPP solution, the maximum values of positioning error Besides, the maximum values of position diferences
are reduced to (2.58, − 3.88, − 4.81) m for GPS, (0.14, are reduced from (21.11, 0.59, 0.89) m to (2.02, − 2.84,
− 2.91, − 7.3) m for GPS + GLONASS, (2.17, − 3.28, − 3.12) m. Compared to the TC multi-GNSS PPP/INS
− 6.12) m for GPS + BDS, and (2.00, − 2.78, − 3.13) m solution, the triple integrated solution achieves a signif-
for GPS + GLONASS + BDS in east, north, and vertical cant improvement in the vertical component but less in
directions, respectively. It can be seen that the position- the horizontal position. Te main reason is that the over-
ing accuracy and availability of the IF PPP solution have all positioning accuracy of the triple integrated system is
Table 4 RMS of position diferences of the PPP solution and the S-VINS aided PPP solution for the GPS, GPS + GLONASS,
GPS + BDS, and GPS + GLONASS + BDS
Items RMS in diferent directions RMS in diferent directions RMS in diferent directions RMS in diferent
for G for G + R for G + C directions for G + R+C
E N U E N U E N U E N U
PPP (m) 1.24 2.54 5.59 1.00 2.35 5.70 1.11 2.40 4.98 0.95 1.95 4.09
S-VINS aided PPP (m) 0.99 1.73 2.49 0.76 1.82 3.17 0.89 1.36 2.60 0.95 1.57 1.32
Improvement (%) 20.2 31.9 55.5 24.0 22.6 44.4 19.8 43.3 47.8 0 19.5 67.7
3D positioning accuracy 49.0 40.3 45.6 51.2
improvement (%)