Page 104 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 104
Shinghal and Bisnath Satell Navig (2021) 2:10 Page 7 of 17
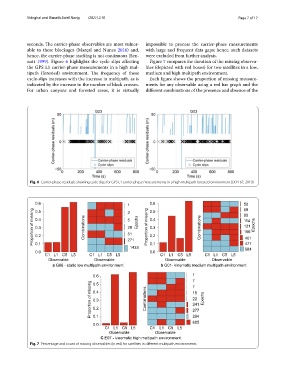
seconds. Te carrier-phase observables are most vulner- impossible to process the carrier-phase measurements
able to these blockages (Marçal and Nunes 2016) and, with large and frequent data gaps; hence, such datasets
hence, the carrier-phase tracking is not continuous (Sen- were excluded from further analysis.
nott 1999). Figure 6 highlights the cycle slips afecting Figure 7 compares the duration of the missing observa-
the GPS L1 carrier-phase measurements in a high mul- bles (depicted with red boxes) for two satellites in a low,
tipath (forested) environment. Te frequency of these medium and high multipath environment.
cycle-slips increases with the increase in multipath, as is Each fgure shows the proportion of missing measure-
indicated by the increase in the number of black crosses. ments for any observable using a red bar graph and the
For urban canyons and forested areas, it is virtually diferent combinations of the presence and absence of the
Fig. 6 Carrier-phase residuals showing cycle slips for GPS L1 carrier-phase measurements in a high multipath forested environment (DOY 67, 2019)
Fig. 7 Percentage and count of missing observables (in red) for satellites in diferent multipath environments