Page 36 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第5期
P. 36
第 5 期 董聪慧, 等: 微液滴在PDMS软基体表面的动态摩擦行为研究 625
200 clinical biochemical analysis systems based on microfluidic driving
Dynamic frictional force /µΝ 160 [ 2 ] 38(2): 183–194 (in Chinese) [袁颖欣, 樊晨, 潘建章, 等. 基于微流
and control technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2020,
控驱动和控制技术的临床生化分析系统研究进展[J]. 色谱, 2020,
38(2): 183–194]. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2019.05006.
Sun Guangtao, Zhang Hongpeng, Gu Changzhi, et al. High precision
120
Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(2): 59–66
80 microfluidic multi-parameter hydraulic oil detection chip design[J].
(in Chinese) [孙广涛, 张洪朋, 顾长智, 等. 高精度微流体多参数液
压油检测芯片设计[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(2): 59–66]. doi:
1.41 1.26 0.41
Elastic modulus/MPa 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804317.
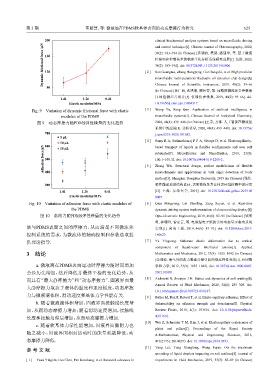
Fig. 9 Variation of dynamic frictional force with elastic [ 3 ] Wang Yu, Fang Qun. Application of artificial intelligence in
modulus of the PDMS microfluidic systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,
图 9 动态摩擦力随PDMS弹性模量的变化趋势 2020, 48(4): 439–448 (in Chinese) [王宇, 方群. 人工智能在微流控
系统中的应用[J]. 分析化学, 2020, 48(4): 439–448]. doi: 10.19756/
700 j.issn.0253-3820.191682.
5 μL
10 μL [ 4 ] Samy R A, Suthanthiraraj P P A, George D, et al. Elastocapillarity-
Adhesion force/μN 500 [ 5 ] substrates[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2019, 23(8):
600
15 μL
based transport of liquids in flexible confinements and over soft
100.1–100.32. doi: 10.1007/s10404-019-2266-2.
Zhang Wei. Structural design, surface modification of flexible
400
microchannels and applications in vital signs detection of body
surface[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2019 (in Chinese) [张伟.
300 柔性微通道的结构设计、表面修饰及其在体表环境检测中的应用
1.41 1.26 0.41 [D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2019]. doi: 10.27012/d.cnki.gdhuu.2019.00
Elastic modulus/MPa 0007.
Fig. 10 Variation of adhesion force with elastic modulus of [ 6 ] Qian Mingyong, Lin Shanling, Zeng Suyun, et al. Real-time
the PDMS dynamic driving system implementation of electrowetting display[J].
图 10 黏附力随PDMS弹性模量的变化趋势 Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(6): 87–95 (in Chinese) [钱明
勇, 林珊玲, 曾素云, 等. 电润湿电子纸的实时动态显示驱动系统
滴与PDMS表面之间的摩擦力,从而满足不同微流体 实现[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(6): 87–95]. doi: 10.12086/oee.2019.
控制系统的需求,为微流体的精确控制和参数选取提 180623.
供理论指导. [ 7 ] Yu Yingsong. Substrate elastic deformation due to vertical
component of liquid-vapor interfacial tension[J]. Applied
3 结论 Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 1025–1042 (in Chinese)
[余迎松. 液气界面张力垂直分量引起的基底弹性变形[J]. 应用数
a. 微液滴在PDMS表面运动时摩擦力随时间增加 学和力学, 2012, 33(9): 1025–1042]. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.
会经历先增加,然后降低并最终平稳的变化趋势,从 2012.09.001.
而具有“最大静摩擦力”和“动态摩擦力”. 固液界面最 [ 8 ] Andreotti B, Snoeijer J H. Statics and dynamics of soft wetting[J].
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 52(1): 285–308. doi:
大静摩擦力取决于液体的黏度和速度梯度,动态摩擦
10.1146/annurev-fluid-010719-060147.
力与微液滴体积、滑动速度和基体力学性能有关.
[ 9 ] Butler M, Box F, Robert T, et al. Elasto-capillary adhesion: Effect of
b. 随着微液滴体积增加,固液界面接触线长度增 deformability on adhesion strength and detachment[J]. Physical
加,从而动态摩擦力增加;随着滑动速度增加,接触线 Review Fluids, 2019, 4(3): 033601. doi: 10.1103/physrevfluids.
4.033601.
长度和接触角滞后增加,从而动态摩擦力增加.
[10] Wei Z, Schneider T M, Kim J, et al. Elastocapillary coalescence of
c. 随着软基体力学性能增加,固液界面黏附力也
plates and pillars[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society
随之减小,固液界面相对运动时的能量耗散降低,动
A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015,
态摩擦力降低. 471(2175): 20140593. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2014.0593.
[11] Yang Lei, Yang Xianglong, Wang Fujun. On the maximum
参 考 文 献
spreading of liquid droplets impacting on soft surfaces[J]. Journal of
[ 1 ] Yuan Yingxin, Fan Chen, Pan Jianzhang, et al. Research advances in Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 33(3): 83–89 (in Chinese)