Page 73 - 《高原气象》2022年第5期
P. 73
高 原 气 象 41 卷
1166
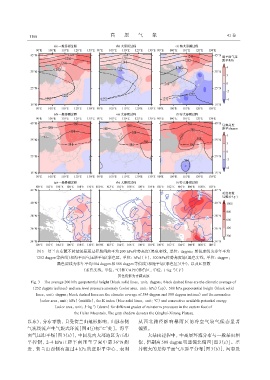
图3 贺兰山东麓不同量级暴雨过程期间的平均200 hPa位势高度(黑色实线,单位:dagpm;黑色虚线为多年平均
1252 dagpm等值线)和海平面气压距平场(彩色区,单位:hPa)(上),500 hPa位势高度场(黑色实线,单位:dagpm;
黑色虚线为多年平均584 dagpm和588 dagpm等值线)和距平场(彩色区)(中),以及K指数
-1
(蓝色实线,单位:℃)和CAPE(彩色区,单位:J·kg )(下)
灰色阴影为青藏高原
Fig. 3 The average 200 hPa geopotential height(black solid lines,unit:dagpm;black dashed lines are the climatic average of
1252 dagpm isolines)and sea level pressure anomaly(color area,unit:hPa)(up),500 hPa geopotential height(black solid
lines,unit:dagpm;black dashed lines are the climatic average of 584 dagpm and 588 dagpm isolines)and the anomalies
(color area,unit:hPa)(middle),the K index(blue solid lines,unit:℃)and convective available potential energy
-1
(color area,unit:J·kg )(down)for different grades of rainstorm processes in the eastern foot of
the Helan Mountain. The gray shadow denotes the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau
以东),分布零散,且受贺兰山地形影响,山脉东侧 从西北路径影响暴雨区的冷空气较气候态显著
气流绕流产生气旋式环流[图 4(j)标“C”处]。海平 偏强。
面气压距平场[图 3(a)],中国境内大部地区为正距 大暴雨过程中,中高层环流分布与一般暴雨相
平控制,2~4 hPa 正距平南压至宁夏中部 36°N 附 似,但副高 588 dagpm 明显偏北偏西[图 3(e)]。差
近,贺兰山西侧有超过 4 hPa 的正距平中心,表明 异较大的是海平面气压距平分布[图 3(b)],河套及