Page 143 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 143
Liu et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:6 Page 10 of 17
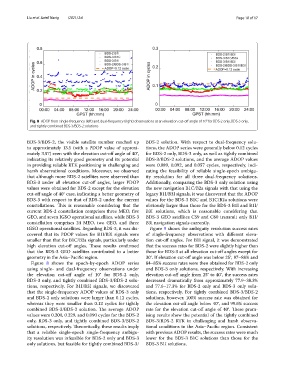
Fig. 8 ADOP from single-frequency (left) and dual-frequency (right) observations at an elevation cut-of angle of 10° for BDS-2 only, BDS-3 only,
and tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solutions
BDS-3/BDS-2, the visible satellite number reached up BDS-2 solution. With respect to dual-frequency solu-
to approximately 13.5 (with a PDOP value of approxi- tions, the ADOP series were generally below 0.12 cycles
mately 3.57) even with the elevation cut-of angle of 40°, for BDS-2 only, BDS-3 only, as well as tightly combined
indicating its relatively good geometry and its potential BDS-3/BDS-2 solutions, and the average ADOP values
in providing reliable RTK positioning in challenging and were 0.089, 0.092, and 0.057 cycles, respectively, indi-
harsh observational conditions. Moreover, we observed cating the feasibility of reliable single-epoch ambigu-
that although more BDS-2 satellites were observed than ity resolution for all three dual-frequency solutions.
BDS-3 under all elevation cut-of angles, larger PDOP Additionally, comparing the BDS-3 only solution using
values were obtained for BDS-2 except for the elevation the new navigation B1C/B2a signals with that using the
cut-of angle of 40° case, indicating a better geometry of legacy B1I/B3I signals, it was discovered that the ADOP
BDS-3 with respect to that of BDS-2 under the current values for the BDS-3 B1C and B1C/B2a solutions were
constellations. Tis is reasonable considering that the obviously larger than those for the BDS-3 B1I and B1I/
current BDS-2 constellation comprises three MEO, fve B3I solutions, which is reasonable considering that
GEO, and seven IGSO operational satellites, while BDS-3 BDS-3 GEO satellites C59 and C60 transmit only B1I/
constellation comprises 24 MEO, two GEO, and three B3I navigation signals currently.
IGSO operational satellites. Regarding BDS-3, it was dis- Figure 9 shows the ambiguity resolution success rates
covered that its PDOP values for B1I/B3I signals were of single-frequency observations with diferent eleva-
smaller than that for B1C/B2a signals, particularly under tion cut-of angles. For B1I signal, it was demonstrated
high elevation cut-of angles. Tese results confrmed that the success rates for BDS-2 were slightly higher than
that the BDS-3 GEO satellites contributed to a better those for BDS-3 at all elevation cut-of angles except for
geometry in the Asia–Pacifc region. 30°. If elevation cut-of angle was below 25°, 87–88% and
Figure 8 shows the epoch-by-epoch ADOP series 84–85% success rates were then obtained for BDS-2 only
using single- and dual-frequency observations under and BDS-3 only solutions, respectively. With increasing
the elevation cut-of angle of 10° for BDS-2 only, elevation cut-of angle from 25° to 40°, the success rates
BDS-3 only, and tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solu- decreased dramatically from approximately 77.9–38.3%
tions, respectively. For B1I/B3I signals, we discovered and 77.6–17.3% for BDS-2 only and BDS-3 only solu-
that the single-frequency ADOP values of BDS-3 only tions, respectively. For tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2
and BDS-2 only solutions were larger than 0.12 cycles, solutions, however, 100% success rate was obtained for
whereas they were smaller than 0.12 cycles for tightly the elevation cut-of angle below 40°, and 99.6% success
combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solution. Te average ADOP rate for the elevation cut-of angle of 40°. Tese prom-
values were 0.200, 0.229, and 0.090 cycles for the BDS-2 ising results show the potential of the tightly combined
only, BDS-3 only, and tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 BDS-3/BDS-2 RTK in challenging and harsh observa-
solutions, respectively. Teoretically, these results imply tional conditions in the Asia–Pacifc region. Consistent
that a reliable single-epoch single-frequency ambigu- with previous ADOP results, the success rates were much
ity resolution was infeasible for BDS-2 only and BDS-3 lower for the BDS-3 B1C solutions than those for the
only solutions, but feasible for tightly combined BDS-3/ BDS-3 B1I solutions.