Page 146 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 146
Liu et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:6 Page 13 of 17
Fig. 14 The average number of observed BDS-3/BDS-2 satellites and their PDOP values during the observation period under diferent elevation
cut-of angles
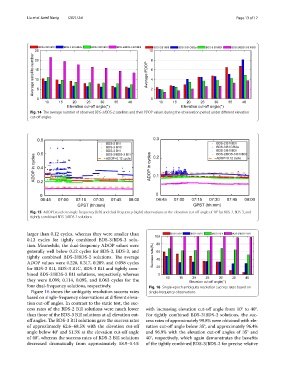
Fig. 15 ADOP based on single-frequency (left) and dual-frequency (right) observations at the elevation cut-of angle of 10° for BDS-2, BDS-3, and
tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solutions
larger than 0.12 cycles, whereas they were smaller than
0.12 cycles for tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solu-
tion. Meanwhile, the dual-frequency ADOP values were
generally well below 0.12 cycles for BDS-2, BDS-3, and
tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solutions. Te average
ADOP values were 0.228, 0.317, 0.209, and 0.098 cycles
for BDS-2 B1I, BDS-3 B1C, BDS-3 B1I and tightly com-
bined BDS-3/BDS-2 B1I solutions, respectively, whereas
they were 0.099, 0.114, 0.095, and 0.063 cycles for the
four dual-frequency solutions, respectively. Fig. 16 Single-epoch ambiguity resolution success rates based on
Figure 16 shows the ambiguity resolution success rates single-frequency observations
based on single-frequency observations at diferent eleva-
tion cut-of angles. In contrast to the static test, the suc-
cess rates of the BDS-2 B1I solutions were much lower with increasing elevation cut-of angle from 10° to 40°.
than those of the BDS-3 B1I solutions at all elevation cut- For tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 solutions, the suc-
of angles. Te BDS-3 B1I solutions gave the success rates cess rates of approximately 99.8% were obtained with ele-
of approximately 62.6–68.5% with the elevation cut-of vation cut-of angle below 35°, and approximately 96.4%
angle below 40° and 51.3% at the elevation cut-of angle and 96.9% with the elevation cut-of angles of 35° and
of 40°, whereas the success rates of BDS-2 B1I solutions 40°, respectively, which again demonstrates the benefts
decreased dramatically from approximately 58.9–5.4% of the tightly combined BDS-3/BDS-2 for precise relative