Page 129 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 129
Xia et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:8 Page 15 of 19
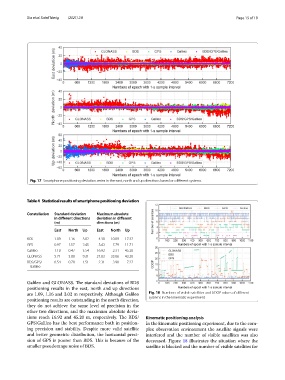
Fig. 17 Smartphone positioning deviation series in the east, north and up directions based on diferent systems
Table 4 Statistical results of smartphone positioning deviation
Constellation Standard deviation Maximum absolute
in diferent directions deviation in diferent
(m) directions (m)
East North Up East North Up
BDS 1.09 1.16 3.02 4.30 10.09 17.37
GPS 0.97 1.57 2.45 5.43 7.79 11.71
Galileo 1.10 0.47 3.54 16.92 2.31 45.20
GLONASS 5.71 5.80 9.31 21.83 33.06 43.20
BDS/GPS/ 0.54 0.70 1.51 2.31 3.90 7.27
Galileo
Galileo and GLONASS. Te standard deviations of BDS
positioning results in the east, north and up directions
are 1.09, 1.16 and 3.02 m respectively. Although Galileo Fig. 18 Numbers of visible satellites and GDOP values of diferent
positioning results are outstanding in the north direction, systems in the kinematic experiment
they do not achieve the same level of precision in the
other two directions, and the maximum absolute devia-
tions reach 16.92 and 45.20 m, respectively. Te BDS/ Kinematic positioning analysis
GPS/Galileo has the best performance both in position- In the kinematic positioning experiment, due to the com-
ing precision and stability. Despite more valid satellite plex observation environment the satellite signals were
and better geometric distribution, the horizontal preci- interfered and the number of visible satellites was also
sion of GPS is poorer than BDS. Tis is because of the decreased. Figure 18 illustrates the situation where the
smaller pseudorange noise of BDS. satellite is blocked and the number of visible satellites for