Page 130 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 130
Xia et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:8 Page 16 of 19
average number of observed satellites is 8.2, 6.1, 3.2 and
0.3, respectively. However, the number of the visible GPS
satellites is more stable. In contrast, the numbers of the
visible BDS and GLONASS satellites vary greatly. Galileo
has only 8 epochs when 4 satellites are observed, and only
1 or 0 satellite visible in most of the observation period.
From the variation trend of the numbers of the visible
BDS and GLONASS satellites, the troughs of their bro-
ken lines correspond to the dense forest areas, indicating
that this harsh environment has the least impact on GPS
signals. Teir GDOP values also confrm this. Te GDOP
values of GPS are small and stable with an average of 2.6,
while those of BDS and GLONASS are very unstable, and
GLONASS is the worst.
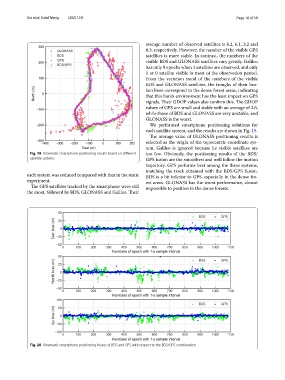
We performed smartphone positioning solutions for
each satellite system, and the results are shown in Fig. 19.
Te average value of GLONASS positioning results is
selected as the origin of the topocentric coordinate sys-
tem. Galileo is ignored because its visible satellites are
Fig. 19 Kinematic smartphone positioning results based on diferent too few. Obviously, the positioning results of the BDS/
satellite systems GPS fusion are the smoothest and well follow the motion
trajectory. GPS performs best among the three systems,
matching the track obtained with the BDS/GPS fusion.
each system was reduced compared with that in the static BDS is a bit inferior to GPS, especially in the dense for-
experiment. est areas. GLONASS has the worst performance, almost
Te GPS satellites tracked by the smartphone were still impossible to position in the dense forests.
the most, followed by BDS, GLONASS and Galileo. Teir
Fig. 20 Kinematic smartphone positioning biases of BDS and GPS with respect to the BDS/GPS combination