Page 124 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 124
Xia et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:8 Page 10 of 19
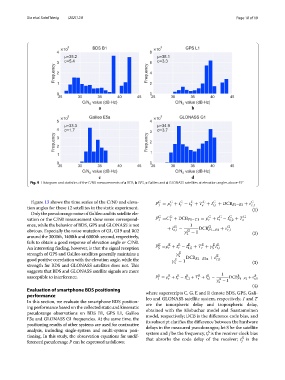
Fig. 9 Histogram and statistics of the C/N0 measurements of a BDS, b GPS, c Galileo and d GLONASS satellites at elevation angles above 45°
Figure 13 shows the time series of the C/N0 and eleva- P = ρ + t − t + T + I C + DCB B1−B3 + ε C
C
C
C
C
C
tion angles for these 12 satellites in the static experiment. 1 r r 3 r r,1 r,1
(1)
Only the pseudorange noise of Galileo and its satellite ele-
G
G
G
G
vation or the C/N0 measurement show some correspond- P =C + DCB P1−C1 = ρ + t − t G + T r G
1
r
1
1,2
r
ence, while the behavior of BDS, GPS and GLONASS is not G 1 G G
obvious. Especially the noise mutation of G1, G19 and R02 + I r,1 − γ − 1 DCB P1−P2 + ε r,1 (2)
G
around the 3000th, 1400th and 6000th second, respectively, 2
fails to obtain a good response of elevation angle or C/N0. E E E E E E E
An interesting fnding, however, is that the signal reception P =ρ + t − t 1,5 + T + γ I
5 r,1
r
r
5
r
strength of GPS and Galileo satellites generally maintains a γ 5 E E
good positive correlation with the elevation angle, while the − γ − 1 DCB E1−E5a + ε r,5
E
strength for BDS and GLONASS satellites does not. Tis 5 (3)
suggests that BDS and GLONASS satellite signals are more
susceptible to interference. P = ρ + t − t R + T + I R − 1 DCB R + ε R
R
R
R
R
1 r r 1,2 r r,1 R P1−P2 r,1
γ − 1
2
(4)
Evaluation of smartphone BDS positioning where superscripts C , G , E and R denote BDS, GPS, Gali-
performance leo and GLONASS satellite system, respectively; I and T
In this section, we evaluate the smartphone BDS position- are the ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay,
ing performance based on the collected static and kinematic obtained with the Klobuchar model and Saastamoinen
pseudorange observations on BDS B1, GPS L1, Galileo model, respectively; DCB is the diference code bias, and
E5a and GLONASS G1 frequencies. At the same time, the its subscript clarifes the diference between the hardware
positioning results of other systems are used for contrastive delays in the measured pseudoranges; let S be the satellite
analysis, including single-system and multi-system posi- system and j be the frequency, t is the receiver clock bias
S
tioning. In this study, the observation equations for undif- that absorbs the code delay of the receiver; t is the
r
S
ferenced pseudorange P can be expressed as follows: j