Page 118 - 卫星导航2021年第1-2合期
P. 118
Xia et al. Satell Navig (2021) 2:8 Page 4 of 19
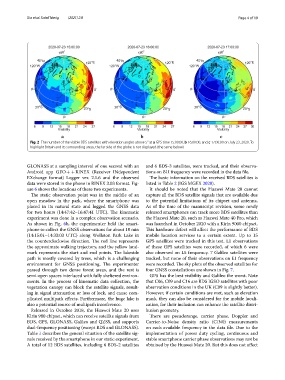
Fig. 2 The number of the visible BDS satellites with elevation angles above 5° at a GPS time 15:00:00, b 16:00:00, and c 17:00:00 on July 23, 2020. To
highlight Britain and its surrounding areas, the far side of the globe is not displayed (the same below)
GLONASS at a sampling interval of one second with an and 6 BDS-3 satellites, were tracked, and their observa-
Android app GEO + + RINEX (Receiver INdependent tions on B1I frequency were recorded in the data fle.
EXchange format) Logger ver. 2.1.6 and the observed Te basic information on the received BDS satellites is
data were stored in the phone in RINEX 3.03 format. Fig- listed in Table 2 (IGS MGEX 2020).
ure 6 shows the locations of these two experiments. It should be noted that the Huawei Mate 20 cannot
Te static observation point was in the middle of an capture all the BDS satellite signals that are available due
open meadow in the park, where the smartphone was to the potential limitations of its chipset and antenna.
placed in its natural state and logged the GNSS data As of the time of the manuscript revision, some newly
for two hours (14:47:42–16:47:41 UTC). Te kinematic released smartphones can track more BDS satellites than
experiment was done in a complex observation scenario. the Huawei Mate 20, such as Huawei Mate 40 Pro, which
As shown in Fig. 6b, the experimenter held the smart- was launched in October 2020 with a Kirin 9000 chipset.
phone to collect the GNSS observations for about 18 min Tis hardware defect will afect the performance of BDS
(14:15:01–14:33:03 UTC) along Wollaton Park Lake in mobile location services to a certain extent. Up to 15
the counterclockwise direction. Te red line represents GPS satellites were tracked in this test. L1 observations
the approximate walking trajectory, and the yellow land- of these GPS satellites were recorded, of which 6 were
mark represents the start and end points. Te lakeside also observed on L5 frequency. 7 Galileo satellites were
path is mostly covered by trees, which is a challenging tracked, but none of their observations on E1 frequency
environment for GNSS positioning. Te experimenter were recorded. Te sky plots of the observed satellites for
passed through two dense forest areas, and the rest is four GNSS constellations are shown in Fig. 7.
semi-open spaces interlaced with fully sheltered environ- GPS has the best visibility and Galileo the worst. Note
ments. In the process of kinematic data collection, the that C06, C09 and C16 are BDS IGSO satellites with poor
vegetation canopy can block the satellite signals, result- observation conditions in the UK (C09 is slightly better).
ing in signal attenuation or loss of lock, and cause com- However, if certain conditions are met, such as elevation
plicated multipath efects. Furthermore, the huge lake is mask, they can also be considered for the mobile locali-
also a potential source of multipath interference. zation, for their inclusion can enhance the satellite distri-
Released in October 2018, the Huawei Mate 20 uses bution geometry.
Kirin 980 chipset, which can receive satellite signals from Tere are pseudorange, carrier phase, Doppler and
BDS, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and QZSS, and supports Carrier-to-Noise density ratio (C/N0) measurements
dual-frequency positioning (except BDS and GLONASS). on each available frequency in the data fle. Due to the
Table 1 describes the general situation of the satellite sig- implementation of power duty cycling, continuous and
nals received by the smartphone in our static experiment. stable smartphone carrier phase observations may not be
A total of 12 BDS satellites, including 6 BDS-2 satellites obtained by the Huawei Mate 20. But this does not afect