Page 127 - 《水产学报》2025年第10期
P. 127
李森栋,等 水产学报, 2025, 49(10): 109609
reduced cortisol levels in blood parrot cichlid and
koi carp, while Aloe vera increased white blood
[51]
cells and lysozyme activity in Nile tilapia . Being
consistent with these, in the present study, the WS
supplement also significantly alleviated the oxidat-
(a) CC (b) CC ive damages and inflammatory responses through
reducing levels of ROS, MDA, and HSP-70, as well
as enhancing SOD activity in fish. Likewise, the WS
dietary could stabilize the immune system of fish
via reducing the immune response and suppressing
the elevation of inflammation factors, IgM, TNF-α
(c) CP (d) CP
and IL-6. These typical cytokines always served as
markers of inflammation activation in previous
studies [13,52] . Taken together, the WS dietary was
found being able to alleviate the stress and immune
responses through reducing the cortisol levels and
suppressing the expression levels of immune related
(e) NC (f) NC
genes in darkbarbel catfish. These findings would
facilitate developing aquatic feed with reduced hep-
atotoxicity and enhanced anti-stress in fish, and
practical strategies for promoting green/health trans-
ition in aquaculture with low cost (CNY 0.5 Yuan
per kg feed for WS supplementation).
(g) NP (h) NP
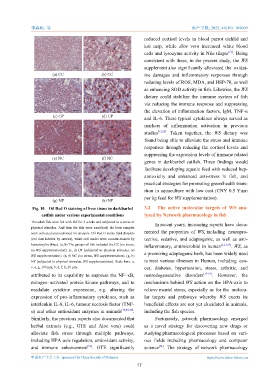
Fig. 10 Oil Red O staining of liver tissue in darkbarbel 3.2 The active molecular targets of WS ana-
catfish under various experimental conditions lyzed by Network pharmacology in fish
The adult fish were fed with WS for 5 weeks and subjected to a stress of
In recent years, increasing reports have docu-
physical stimulus. And then the fish were sacrificed, the liver samples
mented the properties of WS, including neuropro-
were collected and sectioned for analysis. Oil Red O stains lipid droplets
(red dots labeled by arrows), while cell nuclei were counter-stained by tective, sedative, and adaptogenic, as well as anti-
hematoxylin (blue). (a, b) The groups of fish included the CC (no stress, [1,13,53]
inflammatory, antimicrobial in human . WS, as
no WS supplementation); (c, d) CP (subjected to physical stimulus, no
a promising adaptogenic herb, has been widely used
WS supplementation). (e, f) NC (no stress, WS supplementation). (g, h)
NP (subjected to physical stimulus, WS supplementation). Scale bars, a, to treat various illnesses in Human, including can-
c, e, g, 100 µm; b, d, f, h, 20 µm. cer, diabetes, hypertension, stress, arthritic, and
attributed to its capability to suppress the NF‑ κB, neurodegenerative disorders [13-15] . However, the
mitogen‑ activated protein kinase pathways, and to mechanisms behind WS action on the HPA-axis to
modulate cytokine expression, e.g. altering the relieve mental stress, especially as for the molecu-
expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as lar targets and pathways whereby WS exerts its
interleukin IL-8, IL-6, tumour necrosis factor (TNF- beneficial effects are not yet elucidated in animals,
α) and other antioxidant enzymes in animals [10,49-50] . including the fish species.
Similarly, the previous reports also documented that Fortunately, network pharmacology emerged
herbal extracts (e.g., GTE and Aloe vera) could as a novel strategy for discovering new drugs or
alleviate fish stress through multiple pathways, studying pharmacological processes based on vari-
including HPA axis regulation, antioxidant activity, ous fields including pharmacology and computer
[54]
[51]
and immune enhancement . GTE significantly science . The strategy of network pharmacology
中国水产学会主办 sponsored by China Society of Fisheries https://www.china-fishery.cn
17