Page 29 - 《爆炸与冲击》2025年第5期
P. 29
−1.3
=1.00 mm
−1.4
=1.02 mm
−1 −1.2 =0.98 mm
−1.5
−1.6
−1.7
−1.8
−1.9
第 45 卷 柏劲松,等: 端到端机器学习代理模型构建及其在爆轰驱动问题中的应用 第 5 期
/μs
=0.98, 1.00, 1.02 mm
−1.2
−1.3 Simulation data
h=2.45 mm
h=2.50 mm
−1.4
v/(km·s −1 ) −1.5 h=2.55 mm
−1.6
−1.7
−1.8
12 14 16 18 20 22 24
t/μs
(b) Simulated velocity profiles when h=2.45, 2.50, 2.55 mm
图 10 应用代理模型依据速度剖面反向求解 h 值
Fig. 10 Applying the surrogate model to solve the h values according to velocity profiles
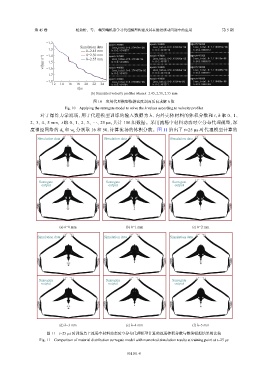
对于爆炸力学流场,用于代理模型训练的输入数据为 h、内外壳体材料的体积分数和 t,h 取 0、1、
2、3、4、5 mm, t 取 0、1、2、3、···、25 µs,共计 156 组数据。采用流场中材料动态时空分布代理模型,深
度神经网络的 d 和 h w 分别取 16 和 50,计算流场的体积分数。图 11 给出了 t=25 µs 时代理模型计算的
h
Simulation data Simulation data Simulation data
Surrogate Surrogate Surrogate
output output output
(a) h=0 mm (b) h=1 mm (c) h=2 mm
Simulation data Simulation data Simulation data
Surrogate Surrogate Surrogate
output output output
(d) h=3 mm (e) h=4 mm (f) h=5 mm
图 11 t=25 µs 时训练点上流场中材料动态时空分布代理模型计算的流场体积分数与数值模拟结果的比较
Fig. 11 Comparison of material distribution surrogate model with numerical simulation results at training point at t=25 μs
051101-8