Page 118 - 《运动与健康科学》(英文)2024年第2期
P. 118
TaggedAPTARAFigure
TaggedAPTARAEnd240 X.R. Tan et al.
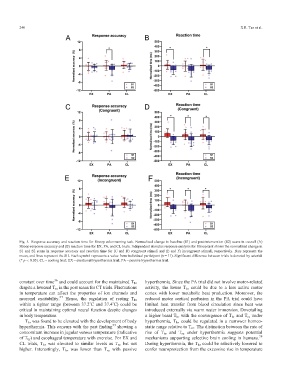
Fig. 5. Response accuracy and reaction time for Stroop color-naming task. Normalized change in baseline (S1) and post-intervention (S2) scans in overall (A)
Stroop response accuracy and (B) reaction time for EX, PA, and CL trials. Independent stimulus response analysis for Stroop task shows the normalized change in
S1 and S2 scans in response accuracy and reaction time for (C and D) congruent stimuli and (E and F) incongruent stimuli, respectively. Bars represent the
mean, and lines represent the SD. Each symbol represents a value from individual participant (n = 11). Significant difference between trials is denoted by asterisk
(* p < 0.05). CL = cooling trial; EX = exertional hyperthermia trial; PA = passive hyperthermia trial.TaggedAPTARAEnd
constant over time 36 and could account for the maintained T br hyperthermia. Since the PA trial did not involve motor-related
despite a lowered T re in the post scans for CT trials. Fluctuations activity, the lower T br could be due to a less active motor
in temperature can affect the properties of ion channels and cortex with lower metabolic heat production. Moreover, the
neuronal excitability. 37 Hence, the regulation of resting T br reduced motor cortical perfusion in the PA trial could have
within a tighter range (between 37.2˚C and 37.4˚C) could be limited heat transfer from blood circulation since heat was
critical in maintaining optimal neural function despite changes introduced externally via warm water immersion. Dovetailing
a higher basal T br with the convergence of T br and T re under
in body temperature.TaggedAPTARAEnd
TaggedAPTARAPT br was found to be elevated with the development of body hyperthermia, T br could be regulated in a narrower homeo-
hyperthermia. This concurs with the past finding 33 showing a static range relative to T re . The distinction between the rate of
concomitant increase in jugular venous temperature (indicative rise of T br and T re under hyperthermia suggests potential
of T br ) and esophageal temperature with exercise. For EX and mechanisms supporting selective brain cooling in humans. 38
CL trials, T br was elevated to similar levels as T re but not During hyperthermia, the T br could be selectively lowered to
higher. Interestingly, T br was lower than T re with passive confer neuroprotection from the excessive rise in temperature