Page 48 - 《摩擦学学报》2020年第6期
P. 48
第 6 期 6 5 m/s 乔小溪, 等: 固-液两相流黑水管道冲蚀磨损的数值模拟研究 731
6
Erosion rate/[10 −8 kg/(m 2 ·s)] 5 4 3 2 6 m/s Erosion rate/[10 −6 kg/(m 2 ·s)] 5 4 3 2 6 m/s
5 m/s
7 m/s
7 m/s
8 m/s
8 m/s
9 m/s
9 m/s
1
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 1 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Degree/(°) Degree/(°)
(a) 2 elbow pipe 5 5 m/s (b) 7 elbow pipe
#
#
Erosion rate/[10 −6 kg/(m 2 ·s)] 3 2 1 6 m/s Erosion rate/[10 −6 kg/(m 2 ·s)] 4 3 2 1 6 m/s
5 m/s
4
7 m/s
7 m/s
8 m/s
8 m/s
9 m/s
9 m/s
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Degree/(°) Length
#
(c) 9 elbow pipe (d) 5 variable diameter pipe
#
# # # #
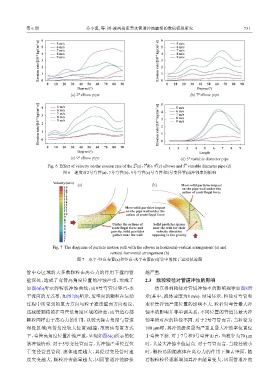
Fig. 6 Effect of velocity on the erosion rate of the 2 (a),7 (b),9 (c) elbows and 5 variable diameter pipe (d)
图 6 速度对2号弯管(a)、7号弯管(b)、9号弯管(c)号弯管和5号变径管(d)冲蚀率的影响
Velocity/(m/s)
(a) (b) Most solid particles impact
19 on the pipe wall under the
18 action of centrifugal force
17
16
15
14
13
12 Most solid particles impact
11 on the pipe wall under the
10 action of centrifugal force
9
8
7 Under the actions of Solid particles sparse
6
5 centrifugal force and near the wall for their
4 gravity, solid particles velocity direction
3 gather near the wall opposing to the gravity
2
1
Fig. 7 The diagrams of particle motion path with the elbows in horizontal-vertical arrangement (a) and
vertical-horizontal arrangement (b)
图 7 水平-竖直布置(a)和竖直-水平布置(b)弯管中的粒子运动轨迹图
管中心区域的大多数颗粒在离心力的作用下撞向管 越严重.
壁深处,造成了弯管高角度位置的冲蚀严重,形成了 2.3 颗粒粒径对管道冲蚀的影响
如图6(b)所示的鞍状冲蚀曲线;而9号弯管以竖直-水 仿真得到粒径对管道冲蚀率的影响规律如图8所
平流向的方式布,如图7(b)所示,近壁面的颗粒在运动 示(其中,流体速度为8 m/s). 结果显示,粒径对弯管和
过程中所受到的重力方向与粒子撞击壁面方向相反, 变径管冲蚀严重位置的影响不大. 粒径对弯管最大冲
这减缓颗粒的在弯管低角度区域的撞击,而管道心部 蚀率的影响并非单调关系,不同位置的管道其最大冲
颗粒同样由于离心力的作用,以较大撞击角度与管道 蚀率所对应的粒径不同. 对于2号弯管而言,当粒径为
深处区域(弯管角度较大位置)碰撞,故而该布置方式 100 μm时,其冲蚀磨损最为严重且最大冲蚀率位置位
下,弯管高角度位置冲蚀严重,呈现如图6(c)所示的驼 于弯管下游. 对于7号和9号弯管而言,当粒径为70 μm
状冲蚀情形. 对于5号变径管而言,其冲蚀严重位置位 时,其最大冲蚀率值最高. 对于弯管而言,当粒径较小
于变径管直管段. 流体速度越大,其经过变径管时速 时,颗粒易跟随流体在离心力的作用下撞击壁面,随
度突变越大,颗粒冲击能量越大,因而管道冲蚀磨损 着颗粒粒径逐渐增加其冲击能量变大,因而管道冲蚀