Page 63 - 《摩擦学学报》2020年第5期
P. 63
618 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 40 卷
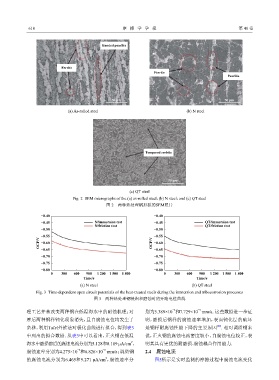
Banded pearlite
Ferrite
Ferrite
Pearlite
50 μm 50 μm
(a) As-rolled steel (b) N steel
Tempered sorbite
50 μm
(c) QT steel
Fig. 2 SEM micrographs of the (a) as-rolled steel,(b) N steel,and (c) QT steel
图 2 两种热处理钢形貌的SEM照片
−0.40 −0.40
−0.45 N/immersion test −0.45 QT/immersion test
N/friction test QT/friction test
−0.50 −0.50
−0.55 −0.55
OCP/V −0.60 OCP/V −0.60
−0.65
−0.65
−0.70 −0.70
−0.75 −0.75
−0.80 −0.80
0 300 600 900 1 200 1 500 1 800 0 300 600 900 1 200 1 500 1 800
Time/s Time/s
(a) N steel (b) QT steel
Fig. 3 Time-dependent open circuit potentials of the heat-treated steels during the immersion and tribocorrosion processes
图 3 两种热处理钢浸泡和磨蚀时的开路电位曲线
−3
−3
理工艺并未改变两种钢在低温海水中的耐蚀机理;对 别为5.389×10 和7.729×10 mm/a. 这些数据进一步证
摩后两种钢样钝化现象消失,且自腐蚀电位均发生了 明,磨损后钢样的腐蚀速率增加,表面钝化层的破坏
[22]
负移,利用Tafel外推法对极化曲线进行拟合,得到表3 是钢样耐腐蚀性能下降的主要原因 . 相对调质钢来
中列出的拟合数据. 从表3中可以看出,正火钢在低温 说,正火钢的腐蚀电流密度较小,自腐蚀电位较正,表
海水中磨损前后的腐蚀电流分别为5.128和8.189 μA/cm , 明其具有更优的耐磨损-腐蚀耦合作用能力.
2
−3
−3
腐蚀速率分别为4.275×10 和6.826×10 mm/a;调质钢 2.4 腐蚀电流
的腐蚀电流分别为6.465和9.271 μA/cm ,腐蚀速率分 图5所示是实时监测的摩擦过程中腐蚀电流变化
2