Page 64 - 《软件学报》2020年第12期
P. 64
3730 Journal of Software 软件学报 Vol.31, No.12, December 2020
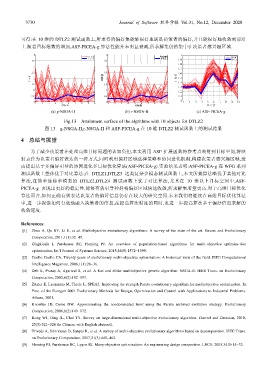
可得:在 10 维的 DTLZ2 测试函数上,所求得的偏好集能够很好地满足决策者的偏好,并且能很好地收敛到前沿
上.随着目标维数的增加,ASF-PICEA-g 算法性能并未明显衰减,所求解集仍然集中在决策者感兴趣区域.
4
求得的解
参考点
3.5
3
2.5
目标值 2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1 2 3 4 5 目标数 6 7 8 9 10
(a) g-NSGA-II (b) r-NSGA-II (c) ASF-PICEA-g
Fig.13 Attainment surface of the algrithms with 10 objects for DTLZ2
图 13 g-NSGA-II,r-NSGA-II 和 ASF-PICEA-g 在 10 维 DTLZ2 测试函数上的测试结果
4 总结与展望
为了减少决策者在处理高维目标问题的认知负担,本文利用 ASF 扩展函数将参考点映射到目标空间,将映
射点作为决策者偏好表达的一种方式,同时利用偏好区域选择策略和协同进化机制,构建决策者感兴趣区域,进
而提出基于多偏好引导的协同进化多目标优化算法(ASF-PICEA-g).实验结果表明:ASF-PICEA-g 在 WFG 系列
测试函数上整体优于对比算法;在 DTLZ1,DTLZ3 这类复杂多模态测试函数上,本文所提算法略优于其他对比
算法,在简单连续单模态的 DTLZ2,DTLZ4 测试函数上优于对比算法,尤其在 10 维以上目标空间中,ASF-
PICEA-g 表现出更好的稳定性,能够有效引导种群朝偏好区域快速收敛,所求解集质量更高.对于高维目标优化
算法而言,如何正确有效表达决策者的偏好信息仍存在较大的研究空间.未来我们将继续在高维目标优化算法
中,进一步探索如何有效地融入决策者的信息,在提高算法精度的同时,也进一步提高算法基于偏好信息求解的
收敛速度.
References:
[1] Zhou A, Qu BY, Li H, et al. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: A survey of the state of the art. Swarm and Evolutionary
Computation, 2011,1(1):32−49.
[2] Giagkiozis I, Purshouse RC, Fleming PJ. An overview of population-based algorithms for multi-objective optimisa-tion
optimisation. Int’l Journal of Systems Science, 2015,46(9):1572−1599.
[3] Coello Coello CA. Twenty years of evolutionary multi-objective optimization: A historical view of the field. IEEE Computational
Intelligence Magazine, 2006,1(1):28−36.
[4] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. on Evolutionary
Computation, 2002,6(2):182−197.
[5] Zitzler E, Laumanns M, Thiele L. SPEA2: Improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective optimization. In:
Proc. of the Eurogen 2001 Evolutionary Methods for Design, Optimization and Control with Applications to Industrial Problems.
Athens, 2001.
[6] Knowles JD, Corne DW. Approximating the nondominated front using the Pareto archived evolution strategy. Evolutionary
Computation, 2006,8(2):149−172.
[7] Kong WJ, Ding JL, Chai TY. Survey on large-dimensional multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Control and Decision, 2010,
25(3):321−326 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Trivedi A, Srinivasan D, Sanyal K, et al. A survey of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition. IEEE Trans.
on Evolutionary Computation, 2017,21(3):440−462.
[9] Fleming PJ, Purshouse RC, Lygoe RJ. Many-objective optimization: An engineering design perspective. LNCS, 2005,3410:14−32.