Page 68 - 《水产学报》2025年第8期
P. 68
万朝阳,等 水产学报, 2025, 49(8): 089306
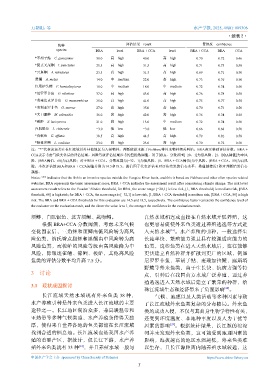
·续表 2·
物种 评估结果 result 置信度 confidence
species BRA level BRA + CCA level BRA + CCA BRA CCA
*革胡子鲇 C. gariepinus 30.0 高 high 40.0 高 high 0.70 0.72 0.46
*斑点叉尾鮰 I. punctatus 25.5 高 high 31.5 高 high 0.71 0.73 0.58
*云斑鮰 A. nebulosus 23.5 高 high 31.5 高 high 0.69 0.71 0.50
黑鮰 A. melas 14.0 中 medium 22.0 高 high 0.73 0.76 0.50
红尾护头鲿 P. hemioliopterus 10.0 中 medium 18.0 中 medium 0.72 0.74 0.50
*尼罗罗非鱼 O. niloticus 37.0 高 high 43.0 高 high 0.76 0.78 0.58
*莫桑比克罗非鱼 O. mossambicus 35.0 高 high 41.0 高 high 0.75 0.77 0.58
*奥利亚罗非鱼 O. aureus 27.0 高 high 35.0 高 high 0.70 0.73 0.50
*大口黑鲈 M. salmoides 36.0 高 high 42.0 高 high 0.76 0.74 0.58
*梭鲈 S. lucioperca 21.0 高 high 13.0 中 medium 0.72 0.74 0.50
白肌银鱼 L. chinensis −3.0 低 low −3.0 低 low 0.66 0.68 0.50
*食蚊鱼 G. affimis 38.5 高 high 44.5 高 high 0.79 0.82 0.58
*眼斑雀鳝 L. oculatus 23.0 高 high 23.0 高 high 0.70 0.72 0.50
注:“*”代表该鱼类在长江流域以外其他地区为入侵物种,判断依据来源于Fishbase等外来物种相关网站。BRA表示基础评估分数,BRA +
CCA表示考虑气候变化后的评估结果。风险等级评估结果参考约登指数阈值,对于BRA,分数范围[−20,1]为低风险,[1,BRA阈值]为中风
险,[BRA阈值,68]为高风险;对于BRA + CCA,分数范围为[−32,1]为低风险,[1,BRA + CCA阈值]为中风险,[BRA + CCA,80]为高风
险。本次评估的BRA和BRA + CCA阈值分别为14.5和18.5。置信因子代表评估者对评估结果的信心水平,数值越接近1即对判断结果信心
越强。
Notes: "*" indicates that the fish is an invasive species outside the Yangtze River basin, and this is based on Fishbase and other alien species related
websites. BRA represents the basic assessment score, BRA + CCA indicates the assessment result after considering climate change. The risk level
assessment result refers to the Youden’ Sindex threshold, for BRA, the score range [−20,1] is low risk, [1, BRA threshold] is medium risk, [BRA
threshold, 68] is high risk; for BRA + CCA, the score range is [−32,1] is low risk, [1, BRA + CCA threshold] is medium risk, [BRA + CCA, 80] is high
risk. The BRA and BRA + CCA thresholds for this evaluation are 14.5 and 18.5, respectively. The confidence factor represents the confidence level of
the evaluator on the evaluation result, and the closer the value is to 1, the stronger the confidence in the evaluation result.
须鲫、白肌银鱼、北方须鳅、匙吻鲟。 自然水域相连或直接在自然水域开展养殖,这
根据 BRA+CCA 分数阈值,考虑未来气候 也更容易促使外来鱼类通过养殖逃逸等方式进
变化因素后,三角鲤和须鲫由低风险转为高风 入天然水域 。水产养殖的引种,一般选择生
[16]
险鱼类,纳氏臀点脂鲤和黑鮰由中风险转为高 长速率快、繁殖能力强且具有较强适应能力的
风险鱼类,而梭鲈的风险等级由高风险降为中 鱼类,这些鱼类在进入天然水域后,往往能够
风险,除眼斑雀鳝、锦鲤、梭鲈,其他高风险 更快建立自然种群并扩散到更广的区域,例如
鱼类的评估分数平均升高 7.5 分。 尼罗罗非鱼、革胡子鲇、麦瑞加拉鲮、露斯塔
野鲮等外来鱼类,由于生长快、抗病力强等特
3 讨论 点,引种后在我国南方水域广泛养殖,通过养
殖逃逸进入天然水域后建立了繁荣的种群,给
3.1 现状成因探讨
珠江流域生态和经济带来了负面影响 。
[28]
长江流域天然水域现有外来鱼类 38 种, 气候、地理以及人类活动等多种因素导致
水产养殖引种是外来鱼类进入长江流域的主要 了长江流域外来鱼类复杂的分布格局。外来鱼
途径之一。长江地区湖泊众多,兼具暖温带和 类的成功入侵,不仅与其自身生物学特性有关,
亚热带等多种气候类型,水产养殖条件得天独 还受到环境温度、本地种丰度以及人为干扰等
厚,使得来自世界各地的鱼类都能在长江流域 因素的影响 。根据统计结果,长江源的沱沱
[29]
找到合适的栖息地。长江流域也是我国水产养 河并未发现外来鱼类,这可能受到地理因素的
殖的重要产区,据统计,仅长江下游,水产养 影响,海拔越高的地区水温越低,外来鱼类难
殖外来鱼类就有 33 种 ,并且养殖水域一般与 以生存,且长江源距离内陆养殖水域较远,这
[14]
中国水产学会主办 sponsored by China Society of Fisheries https://www.china-fishery.cn
7