Page 229 - 《水产学报》2025年第8期
P. 229
何妤如 水产学报, 2025, 49(8): 089319
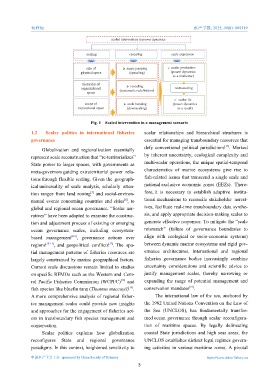
scaled intervention in power dynamics
scaling rescaling scale expression
size of scape jumping scalar production
physical space (upscaling) (power dynamics
as a motivator)
hierarchy of
organizational rescaling restructuring
space (systematic redefinition)
scalar fix
scope of scale bending (power dynamics
expressional space (downscaling) as a result)
Fig. 1 Scaled intervention in a management scenario
1.2 Scalar politics in international fisheries scalar relationships and hierarchical structures is
governance essential for managing transboundary resources that
[15]
defy conventional political jurisdictions . Marked
Globalization and regionalization essentially
by inherent uncertainty, ecological complexity and
represent scale reconstruction that “re-territorializes”
multi-scalar operations, the unique spatial-temporal
State power to larger spaces, with governments as
characteristics of marine ecosystems give rise to
meta-governors guiding extraterritorial power rela-
fish-related issues that transcend a single scale and
tions through flexible scaling. Given the geograph-
ical universality of scale analysis, scholarly atten- national exclusive economic zones (EEZs). There-
[7]
tion ranges from land zoning and social-environ- fore, it is necessary to establish adaptive institu-
[6]
mental events concerning countries and cities , to tional mechanisms to reconcile stakeholder narrat-
global and regional ocean governance. “Scalar nar- ives, facilitate real-time transboundary data synthe-
ratives” have been adopted to examine the construc- sis, and apply appropriate decision-making scales to
tion and adjustment process of existing or emerging generate effective responses. To mitigate the “scale
ocean governance scales, including ecosystem- mismatch” (failure of governance boundaries to
based management [8-9] , governance actions over align with ecological or socio-economic systems)
[12]
regions [10-11] , and geopolitical conflicts . The spa- between dynamic marine ecosystems and rigid gov-
tial management patterns of fisheries resources are ernance architectures, international and regional
largely constrained by marine geographical factors. fisheries governance bodies increasingly combine
Current scale discussions remain limited to studies uncertainty considerations and scientific advice to
on specific RFMOs such as the Western and Cent- justify management scales, thereby narrowing or
[13]
ral Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC) and expanding the range of potential management and
[16]
[14]
fish species like bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii) . conservation mandates .
A more comprehensive analysis of regional fisher- The international law of the sea, anchored by
ies management scales could provide new insights the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of
and approaches for the engagement of fisheries act- the Sea (UNCLOS), has fundamentally transfor-
ors in transboundary fish species management and med ocean governance through scalar reconfigura-
conservation. tion of maritime spaces. By legally delineating
Scalar politics explains how globalization coastal State jurisdictions and high seas areas, the
reconfigures State and regional governance UNCLOS establishes distinct legal regimes govern-
paradigms. In this context, heightened sensitivity to ing activities in various maritime zones. A pivotal
中国水产学会主办 sponsored by China Society of Fisheries https://www.china-fishery.cn
3