Page 52 - 摩擦学学报2025年第5期
P. 52
686 摩擦学学报(中英文) 第 45 卷
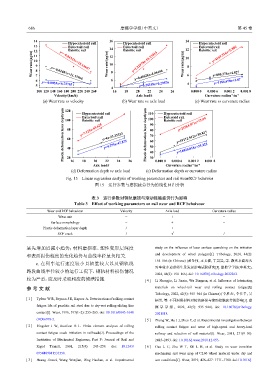
14 Hypoeutectoid rail 16 Hypoeutectoid rail 14 Hypoeutectoid rail
13 Eutectoid rail Eutectoid rail Eutectoid rail
y=4169.516x+5.886
12 Bainitic rail 12 Bainitic rail Bainitic rail
Wear rate/(μg/m) 10 9 8 y=−0.04323x+18.14667 Wear rate/(μg/m) 14 8 y=1.22978x-16.23414 Wear rate/(μg/m) 12 8
11
10
10
y=1184.678x+3.87
6 7 y=−0.02483x+11.33966 6 y=0.48626x-4.06186 6 y=850.374x+4.827
5 y=−0.0053x+6.72763 4 y=0.24318x+0.29576 4
100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 16 18 20 22 24 26 0.000 0 0.000 6 0.001 2 0.001 8
Velocity/(km/h) Axle load/t Curvature radius /m −1
−1
(a) Wear rate vs velocity (b) Wear rate vs axle load Hypoeutectoid rail (c) Wear rate vs curvature radius
120
Plastic deformation layer depth/μm 100 Bainitic rail y=4x-33.33333 Plastic deformation layer depth/μm 100 Bainitic rail
110
Hypoeutectoid rail
Eutectoid rail
Eutectoid rail
y=21564.971x+72.09
y=7.125x-65.625
90
80
80
y=19172.912x+39.817
70
60
y=4.375x-47.875
60
y=14920.818x+35.222
50
40
20
30
20
18
22
0.000 6
0.001 2
16
Axle load/t 24 26 40 0.000 0 Curvature radius /m −1 0.001 8
−1
(d) Deformation depth vs axle load (e) Deformation depth vs curvature radius
Fig. 15 Linear regression analysis of working parameters and rail wear/RCF behavior
图 15 运行参数与磨损疲劳行为的线性回归分析
表 3 运行参数对钢轨磨损与滚动接触疲劳行为影响
Table 3 Effect of working parameters on rail wear and RCF behaivour
Wear and RCF behaviour Velocity Axle load Curvature radius
Wear rate ̶ + ̶
Surface morphology ̶ + ̶
Plastic deformation layer depth / + ̶
RCF crack / √ /
呈先增加后减小趋势;材料磨损率、塑性变形层深度 study on the influence of laser surface quenching on the initiation
和表面损伤程度的变化趋势与曲线半径呈负相关. and development of wheel polygon[J]. Tribology, 2024, 44(2):
154–166 (in Chinese) [黄金伟, 王文健, 丁昊昊, 等. 激光表面淬火
c. 在列车运行速度较小且轴重较大以及钢轨线
对车轮多边形萌生及发展影响试验研究[J]. 摩擦学学报(中英文),
路段曲线半径较小的运行工况下,钢轨材料损伤情况
2024, 44(2): 154–166]. doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.2022262.
较为严重,应及时采取相应的修缮措施. [ 4 ] Li Shengjie, Li Jiaxin, Wu Bingnan, et al. Influence of lubricating
materials on wheel-rail wear and rolling contact fatigue[J].
参 考 文 献
Tribology, 2022, 42(5): 935–944 (in Chinese) [李胜杰, 李佳辛, 吴
[ 1 ] Tyfour W R, Beynon J H, Kapoor A. Deterioration of rolling contact
柄男, 等. 不同润滑材料对轮轨磨损与滚动接触疲劳的影响[J]. 摩
fatigue life of pearlitic rail steel due to dry-wet rolling-sliding line
擦 学 学 报 , 2022, 42(5): 935–944]. doi: 10.16078/j.tribology.
contact[J]. Wear, 1996, 197(1–2): 255–265. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648
2021118.
(96)06978-5. [ 5 ] Zhong W, Hu J J, Shen P, et al. Experimental investigation between
[ 2 ] Ringsber J W, Josefson B L. Finite element analyses of rolling rolling contact fatigue and wear of high-speed and heavy-haul
contact fatigue crack initiation in railheads[J]. Proceedings of the railway and selection of rail material[J]. Wear, 2011, 271(9–10):
Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and 2485–2493. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2010.12.053.
Rapid Transit, 2001, 215(4): 243–259. doi: 10.1243/ [ 6 ] Guo L C, Zhu W T, Shi L B, et al. Study on wear transition
0954409011531558. mechanism and wear map of CL60 wheel material under dry and
[ 3 ] Huang Jinwei, Wang Wenjian, Ding Haohao, et al. Experimental wet conditions[J]. Wear, 2019, 426–427: 1771–1780. doi:10.1016/j.