Page 78 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第5期
P. 78
第 5 期 林国志, 等: 表面微织构对WC-8Co在往复摩擦磨损中粘结-扩散磨损特性的影响 667
P P
Sliding direction Sliding direction
Ti6Al4V sphere Ti6Al4V sphere
Ti6Al4V debris
Micro-groove Convex region Scattered adhesion trapped in the
Ti6Al4V debris
WC grain WC grain interface
captured by the
Co binder micro-groove Co binder
P P
Sliding direction Sliding direction
Ti6Al4V sphere Slight adhesion Ti6Al4V sphere
Micro-groove on the convex region Severe adhesion
on the surface
WC grain Filling/adhering layer WC grain
Co binder Co binder
(a) (b)
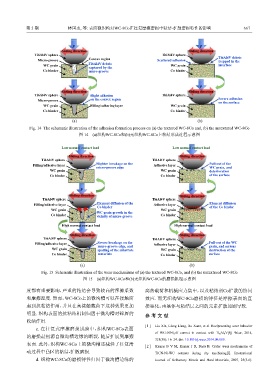
Fig. 14 The schematic illustration of the adhesion formation process on (a) the textured WC-8Co and, (b) the untextured WC-8Co
图 14 (a)织构WC-8Co和(b)无织构WC-8Co上粘结形成过程示意图
Low normal contact load Low normal contact load
Sliding direction Sliding direction
Ti6Al4V sphere Ti6Al4V sphere
Slighter breakage on the Pull-out of the
Filling/adhesive layer Adhesive layer
micro-groove edge WC grain, and
WC grain WC grain deterioration
Co binder Co binder of the surface
P P
Sliding direction Sliding direction
Ti6Al4V sphere Ti6Al4V sphere
Filling/adhesive layer Element diffusion of the Adhesive layer Element diffusion
Co binder of the Co binder
WC grain WC grain
WC grain growth in the
Co binder vicinity of micro-groove Co binder
High normal contact load High normal contact load
Sliding direction Sliding direction
Ti6Al4V sphere Ti6Al4V sphere
Filling/adhesive layer Severe breakage on the Adhesive layer Pull-out of the WC
micro-groove edge, and grain, and serious
WC grain spalling of the substrate WC grain destruction of the
Co binder materials Co binder surface
(a) (b)
Fig. 15 Schematic illustration of the wear mechanisms of (a) the textured WC-8Co, and (b) the untextured WC-8Co
图 15 (a)织构WC-8Co和(b)无织构WC-8Co的磨损机理示意图
度都有重要影响,严重的粘结会导致较高的摩擦系数 高热载荷和机械应力集中,以及粘结剂Co扩散的协同
和摩擦温度. 然而,WC-8Co上的微沟槽可以在接触面 效应. 而无织构WC-8Co磨损的特征是摩擦表面的直
起到抗粘结作用,并且在高接触载荷下这种效果更加 接恶化,由基体与粘结层之间的元素扩散加剧导致.
明显. 织构表面的抗粘结机制归因于微沟槽对碎屑的
参 考 文 献
收纳作用.
[ 1 ] Liu Xin, Liang Liang, Xu Xuan, et al. Reciprocating wear behavior
c. 在往复式摩擦磨损试验中,织构WC-8Co表面
of WC-10Ni 3 Al cermet in contact with Ti 6 Al 4 V[J]. Wear, 2014,
的磨损最初源自微沟槽边缘的断裂,随后扩展到摩擦
321(30): 16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2014.09.009.
表面. 此外,织构WC-8Co上的微沟槽还减轻了往复滑
[ 2 ] Kumar B V M, Kumar J R, Basu B. Crater wear mechanisms of
动过程中凸区的粘结-扩散磨损. TiCN-Ni-WC cermets during dry machining[J]. International
d. 织构WC-8Co的磨损特性归因于微沟槽边缘的 Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2007, 25(5-6):