Page 23 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第3期
P. 23
312 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 41 卷
100 μm
500 μm C
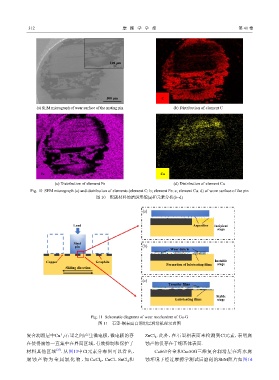
(a) SEM micrograph of wear surface of the mating pin (b) Distribution of element C
Fe Cu
(c) Distribution of element Fe (d) Distribution of element Cu
Fig. 10 SEM micrograph (a) and distribution of elements (element C: b; element Fe: c; element Cu: d) of worn surface of the pin
图 10 配副材料的磨斑形貌(a)和元素分析(b~d)
(a)
Load Asperities Incipient
stage
Steel
pin (b)
Wear debris
Copper Graphite Instable
Formation of lubricating films stage
Sliding direction
(c)
Transfer films
Stable
Lubricating films stage
Fig. 11 Schematic diagrams of wear mechanism of Cu-G
图 11 石墨-铜表面自润滑层润滑机理示意图
复合润滑层中Cu与石墨之间产生微电极,微电极的存 ZnCl . 此外,在石墨相表面未检测到Cl元素,表明腐
2
在使得腐蚀一直集中在界面区域,有效抑制和保护了 蚀产物仅存在于铜基体表面.
[25]
材料其他区域 . 从图13中Cl元素分布图可以看出, Cu663合金和Cu-50G三维复合润滑层在海水腐
腐 蚀 产 物 为 金 属 氯 化 物 , 如 CuCl 、 CuCl、 SnCl 和 蚀环境下经过摩擦学测试后磨斑的SEM照片如图14
2
2