Page 127 - 《运动与健康科学》(英文)2024年第2期
P. 127
TaggedAPTARAEndExPlas promotes neurogenesis in AD rat brain TaggedAPTARAFigure 249
MD, USA) and a tailored script. For more details, see
Supplementary Materials.TaggedAPTARAEnd
TaggedAPTARAH22.13. Immunofluorescent staining and quantification for
neurogenesis analysisTaggedAPTARAEnd
TaggedAPTARAPFor quantification of neurogenesis, 7 brain sections with
intersection distance 240 mm were co-labeled with immunoflu-
orescence markers of cellular proliferation (BrdU) and mature
neurons (hexaribonucleotide binding protein-3 (NeuN)).
Sections were incubated with primary antibodies (BrdU mouse
monoclonal antibody and NeuN rabbit monoclonal antibody)
at 4˚C overnight. The following day, the sections were incu-
bated for 60 min in a solution of Tris-buffered saline
containing fluorescently conjugated secondary antibodies
(Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L Alexa Fluor 488 and Goat anti-
Rabbit IgG H&L Alexa Fluor 594) and mounted on SuperFrost
Plus Adhesion Slides (Thermo Fisher Scientific).TaggedAPTARAEnd
TaggedAPTARAPFor all sections, Z-stack images of the dorsal dentate gyrus
29
(bregma range 3.14 to 4.52 ) were bilaterally imaged with
Zeiss 880 Airyscan Confocal Microscope (Carl Zeiss AG,
Oberkochen, Germany). The Zen image-acquisition software
(Carl Zeiss AG) enabled a reusable imaging routine setup with
the experiment designer module. The image analyses for quan-
tification of neurons and neurogenesis were done using Fiji
30
software. For more details, see Supplementary Materials.TaggedAPTARAEnd
TaggedAPTARAH22.14. Statistical analysesTaggedAPTARAEnd
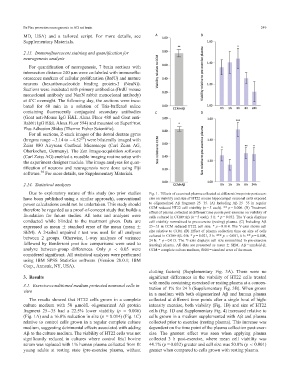
TaggedAPTARAPDue to exploratory nature of this study (no prior studies Fig. 1. Effects of exercised plasma collected at different timepoints post-exer-
have been published using a similar approach), conventional cise on viability and size of HT22 mouse hippocampal neuronal cells exposed
power calculations could not be undertaken. This study should to oligomerized Ab fragment 2535. (A) Including Ab 2535 in regular
CCM reduced HT22 cell viability (n = 5 each). ** p = 0.006. (B) Treatment
therefore be regarded as a proof-of-concept study that builds a
effect of plasma collected at different time points post-exercise on viability of
foundation for future studies. All tests and analyses were cells cultured in CCM+Ab (n = 5 each). 3 h: * p = 0.032. The Y-axis displays
conducted while blinded to the treatment given. Data are cell viability normalized to pre-exercise (resting) plasma. (C) Including Ab
expressed as mean § standard error of the mean (mean § 2535 in CCM reduced HT22 cell size. * p = 0.014. The Y-axis shows cell
SEM). A 2-tailed unpaired t test was used for all analyses size relative to CCM. (D) Effect of plasma collection time on size of cells
cultured in CCM+Ab. 0 h: * p = 0.021, 3 h: *** p < 0.001, 6 h: ** p = 0.008,
between 2 groups. Otherwise, 1-way analyses of variance
24 h: * p = 0.013. The Y-axis displays cell size normalized to pre-exercise
followed by Bonferroni post hoc comparisons were used to (resting) plasma. All data are presented as mean § SEM. Ab = amyloid-b;
analyze between-group differences. Only p < 0.05 were CCM = complete culture medium; SEM = standard error of the mean.TaggedAPTARAEnd
considered significant. All statistical analyses were performed
using IBM SPSS Statistics software (Version 28.0.1; IBM
Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).TaggedAPTARAEnd
clotting factors) (Supplementary Fig. 3A). There were no
significant differences in the viability of HT22 cells treated
TaggedAPTARAH13. ResultsTaggedAPTARAEnd
with media containing exercised or resting plasma at a concen-
TaggedAPTARAH23.1. Exercise-conditioned medium protected neuronal cells in
tration of 1% for 24 h (Supplementary Fig. 3B). When grown
vitroTaggedAPTARAEnd
in a medium with both oligomerized Ab and human plasma
TaggedAPTARAPThe results showed that HT22 cells grown in a complete collected at different time points after a single bout of high-
culture medium with 50 mmol/L oligomerized Ab protein intensity exercise, both viability (Fig. 1B) and size of HT22
fragment 2535 had a 22.5% lower viability (p= 0.006) cells (Fig. 1D and Supplementary Fig. 4) increased relative to
(Fig. 1A) and a 16.8% reduction in size (p= 0.014) (Fig. 1C) cells grown in a medium supplemented with Ab and plasma
relative to control cells grown in a regular complete culture collected prior to exercise (resting plasma). This increase was
medium, suggesting detrimental effects associated with adding dependent on the time point of the plasma collection post-exer-
Ab to the culture medium. The viability of HT22 cells was not cise. The greatest effect was seen when applying plasma
significantly reduced in cultures where control fetal bovine collected 3 h post-exercise, where mean cell viability was
serum was replaced with 1% human plasma collected from fit 44.1% (p = 0.032) greater and cell size was 50.0% (p < 0.001)
young adults at resting state (pre-exercise plasma, without greater when compared to cells grown with resting plasma.TaggedAPTARAEnd