Page 80 - 《水产学报》2025年第8期
P. 80
王一航,等 水产学报, 2025, 49(8): 089307
2.0 1
1龄 1-year-old
2龄 2-year-old 0
耗氧率/[mg/(g DW·h)] oxygen consumption rate 1.0 耗氧率的对数 logarithm of oxygen consumption rate −1
3龄 3-year-old
1.5
−2
0.5
0.003 3
0 5 10 15 20 25 −3 0.003 4 0.003 5 0.003 6
温度/°C 热力学温度倒数
temperature reciprocal temperature
(a) (b)
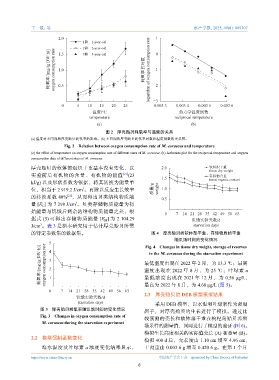
图 2 厚壳贻贝耗氧率与温度的关系
(a) 温度对不同规格厚壳贻贝耗氧率的影响,(b) 不同规格厚壳贻贝耗氧率对数和温度倒数的关系图。
Fig. 2 Relation between oxygen consumption rate of M. coruscus and temperature
(a) the effect of temperature on oxygen consumption rate of different sizes of M. coruscus; (b) Arrhenius plot for the reciprocal temperature and oxygen
consumption data of different sizes of M. coruscus.
厚壳贻贝的软体部组织干重基本没有变化,以 2.0 软组织干重
tissue dry weight
实验前后有机物的含量、有机物的能值 [21] (23 有机物含量
1.5 tissue organic content
kJ/g) 以及形状系数为依据,将其转换为能量单
位,相当于 2 919.2 J/cm 。再除以反应生长效率 质量/g weight 1.0
3
[21]
的转换系数 40% ,从而得出贝类结构物质能 0.5
量 [E ] 为 7 298 J/cm 。贝类存储物质能量为初
3
G
始能量与饥饿后剩余的结构物质能量之差,根
0 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63
据式 (5) 可得出存储物质能量 [E ] 为 2 104.29
M 饥饿实验天数/d
J/cm 。表 3 是指本研究用于估计厚壳贻贝所需 starvation days
3
的特定参数集的数据集。 图 4 厚壳贻贝的软体部干重、存储物质的干重
随饥饿时间的变化情况
5 4 Fig. 4 Changes in tissue dry weight, storage of reserves
耗氧率/[mg/(g DW·h)] oxygen consumption rate 3 2 1 最低温度出现在 2022 2022 8 年 月,为 月,为 25 ℃;叶绿素 a
in the M. coruscus during the starvation experiment
13.3 ℃;最高
2
温度出现在
年
月,为
最低浓度出现在
年
0.56 μg/L,
2021
12
0 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 最高为 2022 年 8 月,为 4.68 μg/L (图 5)。
2.3 厚壳贻贝的 DEB 模型模拟结果
饥饿实验天数/d
starvation days 采用 DEB 模型,以水温和叶绿素作为强制
图 3 厚壳贻贝耗氧率随饥饿时间的变化情况 因子,对厚壳贻贝的生长进行了模拟。通过比
Fig. 3 Changes in oxygen consumption rate of
较预测的壳长和软体部干重在枸杞岛贻贝养殖
M. coruscus during the starvation experiment 场采样的测量值,同时进行了模型的验证 (图 6)。
模拟生长高度相关的实际值壳长 (A) 和重量 (B)。
2.2 模型强制函数变化
模拟 400 d 后,壳长度由 1.10 cm 增至 4.96 cm,
海水温度及叶绿素 a 浓度变化结果显示, 干肉重由 0.003 6 g 增至 0.420 6 g。在第 1 个月
https://www.china-fishery.cn 中国水产学会主办 sponsored by China Society of Fisheries
6