Page 169 - 《软件学报》2024年第4期
P. 169
钱鸿 等: 基于动态批量评估的绿色无梯度优化方法 1747
(a) Housing (b) Housing (分析) (c) SST-2 低维 (d) SST-2 低维(泛化)
(e) SST-2 低维(分析) (f) SST-2 高维 (g) SST-2 高维(泛化) (h) SST-2 高维(分析)
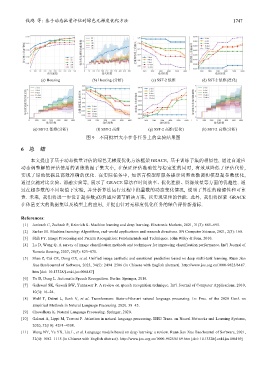
图 9 不同批量大小在各任务上的实验结果图
6 总 结
本文提出了基于动态批量评估的绿色无梯度优化方法框架 GRACE, 基于训练子集的相似性, 通过自适应
动态调整解的评估使用的训练数据子集大小, 在保证评估准确性与稳定性的同时, 有效地降低了评估代价,
实现了绿色低碳且高效准确的优化. 在实际任务中, 如语言模型即服务提示词黑盒微调和模型超参数优化,
通过实施对比实验、消融实验等, 展示了 GRACE 算法在时间效率、优化性能、资源效益等方面的优越性. 通
过在超参数的不同取值下实验, 并分析算法运行过程中批量数的动态变化情况, 说明了算法的稳健性和可靠
性. 未来, 我们将进一步设计超参数γ的自适应调节解决方案, 以实现更佳的性能. 此外, 我们将探索 GRACE
在体量更大的数据集以及模型上的应用, 并提出针对无梯度优化任务的绿色评价新指标.
References:
[1] Janiesch C, Zschech P, Heinrich K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electronic Markets, 2021, 31(3): 685−695.
[2] Sarker IH. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Computer Science, 2021, 2(3): 160.
[3] Shih FY. Image Processing and Pattern Recognition: Fundamentals and Techniques. John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
[4] Lu D, Weng Q. A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int’l Journal of
Remote Sensing, 2007, 28(5): 823−870.
[5] Shen Z, Cui CR, Dong GX, et al. Unified image aesthetic and emotional prediction based on deep multi-task learning. Ruan Jian
Xue Bao/Journal of Software, 2023, 34(5): 2494−2506 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/6487.
htm [doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006487]
[6] Yu D, Deng L. Automatic Speech Recognition. Berlin: Springer, 2016.
[7] Gaikwad SK, Gawali BW, Yannawar P. A review on speech recognition technique. Int’l Journal of Computer Applications, 2010,
10(3): 16−24.
[8] Wolf T, Debut L, Sanh V, et al. Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing. In: Proc. of the 2020 Conf. on
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2020. 38−45.
[9] Chowdhary K. Natural Language Processing. Springer, 2020.
[10] Galassi A, Lippi M, Torroni P. Attention in natural language processing. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,
2020, 32(10): 4291−4308.
[11] Wang NY, Ye YX, Liu L, et al. Language models based on deep learning: a review. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/Journal of Software, 2021,
32(4): 1082−1115 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/6169.htm [doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006169]