Page 157 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第5期
P. 157
746 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 41 卷
120 120
ε=10% ε=10%
100 100
ε=50% 80 ε=50%
Pressure difference/kPa 60 Pressure difference/kPa 60
ε=90%
ε=90%
80
40
40
20
20
−20 0 −20 0
−40 −40
0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.8 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0 0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.8 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0
Axial distance/mm Axial distance/mm
(a) Hybrid labyrinth-honeycomb seal (b) Traditional labyrinth seal
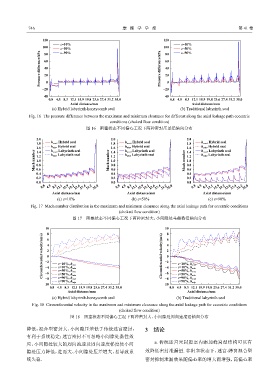
Fig. 16 The pressure difference between the maximum and minimum clearance for different along the axial leakage path eccentric
conditions (choked flow condition)
图 16 阻塞状态不同偏心工况下两种密封压差沿轴向分布
2.0 2.0 2.0
h max , Hybrid seal h max , Hybrid seal h max , Hybrid seal
1.8 1.8 1.8
1.6 h min , Hybrid seal 1.6 h min , Hybrid seal 1.6 h min , Hybrid seal
Mach number 1.2 h min , Labyrinth seal Mach number 1.2 h min , Labyrinth seal Mach number 1.2 h min , Labyrinth seal
h max , Labyrinth seal
h max , Labyrinth seal
h max , Labyrinth seal
1.4
1.4
1.4
1.0
1.0
1.0
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.6
0.4 0.6 0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2 0.2 0.2
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.2 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0 0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.2 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0 0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.2 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0
Axial distance/mm Axial distance/mm Axial distance/mm
(a) ε=10% (b) ε=50% (c) ε=90%
Fig. 17 Mach number distribution in the maximum and minimum clearance along the axial leakage path for eccentric conditions
(choked flow condition)
图 17 阻塞状态不同偏心工况下两种密封大、小间隙处马赫数沿轴向分布
10 8 6 10 8 6
Circumferential velocity/(m/s) −2 4 2 0 ε=10%, h max Circumferential velocity/(m/s) −2 4 2 0 ε=10%, h max
−4
−4
ε=10%, h min
ε=10%, h min
−6
−6
ε=50%, h min
ε=50%, h min
−8
−8
ε=90%, h max
ε=90%, h max
−10 ε=50%, h max −10 ε=50%, h max
ε=90%, h min
ε=90%, h min
0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.8 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0 0.8 4.5 8.3 12.1 15.9 19.8 23.6 27.4 31.2 35.0
Axial distance/mm Axial distance/mm
(a) Hybrid labyrinth-honeycomb seal (b) Traditional labyrinth seal
Fig. 18 Circumferential velocity in the maximum and minimum clearance along the axial leakage path for eccentric conditions
(choked flow condition)
图 18 阻塞状态不同偏心工况下两种密封大、小间隙处周向速度沿轴向分布
降低,混合型密封大、小间隙压差低于传统迷宫密封, 3 结论
有利于系统稳定;迷宫密封不可忽略小间隙处黏性效
应,小间隙处较大的周向流速及周向速度梯度使小间 a. 传统迷宫密封腔室内添加蜂窝型结构可以有
隙处压力降低,进而大、小间隙处压差增大,易导致系 效降低密封泄漏量. 非阻塞状态下,迷宫-蜂窝混合型
统失稳. 密封抑制泄漏效果随偏心率的增大而增强,高偏心率