Page 138 - 《摩擦学学报》2020年第4期
P. 138
548 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 40 卷
3.4.4 织构排间距 进行了流场分析.
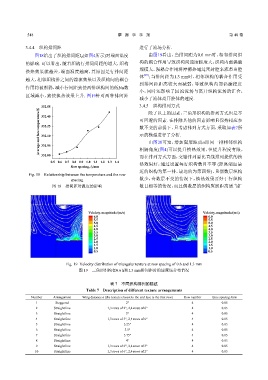
图18给出了织构排间距l (如图4所示)对端面温度 由图19看出,当排间距为0.6 mm时,相邻排间织
2
的影响. 可以看出,随着织构行排间间距的增大,织构 构的耦合作用导致织构间速度梯度大,织构内部涡漩
规模大,强耦合作用将摩擦热通过密封腔来流带出腔
换热效果就越差,端面温度越高,其原因是行排间距
[26]
体 ;当排间距为1.3 mm时,相邻织构的耦合作用受
越大,相邻织构排之间的湍流效果以及织构间的耦合
到排间距距离较大而减弱,导致织构内部涡漩程度
作用将被削弱,减小行间距致使两排织构间的低Nu数
小,同时还影响了回流流场与离开织构流场的汇合,
区域减小,致使换热效果上升. 图19针对两种排间距
减小了流体离开腔体的速度.
3.4.5 织构排列方式
332.55 除了以上的因素,三角形织构的排列方式也是不
Average end face temperature/K 332.25 可回避的因素. 在排除其他的因素影响且保持相应参
332.40
数不变的前提下,只考虑排列方式方面,采取如表7所
示的模型进行了分析.
332.10
由图20可知,增加翼展距离α即同一排相邻织构
331.95
相隔角度(图4)可以提升换热效果,但提升程度有限,
331.80
而在排列方式方面,交错排列要比直线排列提供的换
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 热效果好,通过设置每行织构数目不等 (距离端面最
Row spacing, l 2 /mm
近的织构为第一排,最远的为第四排),且偶数层织构
Fig. 18 Relationship between the temperature and the row
spacing 数少,奇数层不变的情况下,换热效果要好于行织构
图 18 排间距对温度的影响 数目相等的情况,而且偶数层的织构翼展距离适当扩
Veloicty-magnitude/(m/s) Veloicty-magnitude/(m/s)
6.0 6.0
5.5 5.5
5.0 5.0
4.5 4.5
4.0 4.0
3.5 3.5
3.0 3.0
2.5 2.5
2.0 2.0
1.5 1.5
1.0 1.0
0.5 0.5
Fig. 19 Velocity distribution of triangular texture at row spacing of 0.6 and 1.3 mm
图 19 三角形织构在0.6 h和1.3 mm排间距时的速度场分布情况
表 7 不同织构排列的描述
Table 7 Description of different texture arrangements
Number Arrangement Wing distance α (the texture closest to the end face is the first row) Row number Line spacing /mm
1 Staggered 2° 4 0.85
2 Straight line 1,3 rows of 2°, 2,4 rows of 6° 4 0.85
3 Straight line 3° 4 0.85
4 Straight line 1,3 rows of 3°, 2,4 rows of 6° 4 0.85
5 Straight line 3.25° 4 0.85
6 Straight line 3.5° 4 0.85
7 Straight line 3.75° 4 0.85
8 Straight line 4° 4 0.85
9 Straight line 1,3 rows of 6°, 2,4 rows of 3° 4 0.85
10 Straight line 1,3 rows of 6°, 2,4 rows of 2° 4 0.85