Page 70 - 《高原气象》2023年第1期
P. 70
高 原 气 象 42 卷
66
Guo Y P, Wang C H, 2014. Trends in precipitation recycling over the
Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in last decades[J]. Journal of Hydrolo‐
gy, 517: 826-835. DOI: 10. 1016/j. jhydrol. 2014. 06. 006.
Hu J, Duan A M, 2015. Relative contributions of the Tibetan Plateau
thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature ba‐
sin mode to the interannual variability of the East Asian summer
monsoon [J]. Climate Dynamics, 45(9-10): 2697-2711. DOI:
10. 1007/s00382-015-2503-7.
Luo Y L, Zhang R H, Qian W M, et al, 2011. Intercomparison of
deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau-Asian Monsoon Region
and Subtropical North Amercia in boreal summer using CloudSat/
CALIPSO Data[J]. Journal of Climate, 24(8): 2164-2177.
DOI: 10. 1175/2010JCLI4032. 1.
Schneider U, Becker A, Finger P, et al, 2014. GPCC's new land sur‐
face precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in situ
data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle[J]. Theoret‐
ical and Applied Climatology, 115(S1/2) : 15-40. DOI:
10. 1007/s00704-013-0860-x.
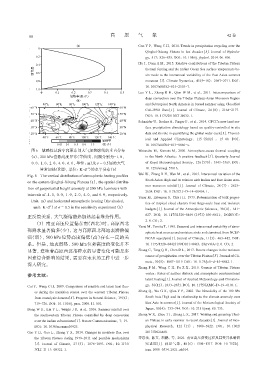
图6 敏感性试验中高原东部大气加热廓线的垂直分布 Watanabe M, Kimoto M, 2000. Atmosphere-ocean thermal coupling
(a), 200 hPa位势高度异常(等值线, 间隔分别为-1. 0、 in the North Atlantic: A positive feedback[J]. Quarterly Journal
0. 0、 1. 0、 2. 0、 4. 0、 6. 0, 单位: m)及σ = 0.5层的大气 of Royal Meteorological Society, 126(570): 3343-3369. DOI:
异常加热(阴影, 单位: K·d )的水平分布(b) 10. 1256/smsqj. 57016.
-1
Fig. 6 The vertical distribution of atmospheric heating profiles Wei W, Zhang R H, Wen M, et al, 2015. Interannual variation of the
South Asian High and its relation with Indian and East Asian sum‐
on the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (a), the spatial distribu‐
mer monsoon rainfall[J]. Journal of Climate, 28(7): 2623-
tion of geopotential height anomaly at 200 hPa (contours with
2634. DOI: 10. 1175/JCLI-D-14-00454. 1.
intervals of -1. 0, 0. 0, 1. 0, 2. 0, 4. 0, and 6. 0, respectively.
Yanai M, Esbensen S, Chu J H, 1973. Determination of bulk proper‐
Unit: m) and horizontal atmospheric heating (the shaded,
ties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture
-1
unit: K·d ) at σ = 0.5 in the sensitivity experiment (b) budgets[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 30(4): 611-
正反馈关系, 大气凝结潜热加热起着维持作用。 627. DOI: 10. 1175/1520-0469(1973)030<0611: DOBPOT>
2. 0. CO; 2.
(3) 南亚高压位置偏东南(西北)时, 高原西北
Yanai M, Tomita T, 1998. Seasonal and interannual variability of atmo‐
部降水显著偏多(少), 这与高原西北部地表潜热偏
spheric heat sources and moisture sinks as determined from NCEP-
强(弱), 500 hPa 位势高度偏低(高)存在一定的关 NCAR reanalysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 11(3): 463-482. DOI:
系。但是, 地表潜热、 500 hPa位势高度的变化并不 10. 1175/1520-0442(1998)011<0463: SAIVOA>2. 0. CO; 2.
显著, 意味着高原西北部降水的显著变化可能是多 Zhang C, Tang Q H, Chen D L, 2017. Recent changes in the moisture
因素综合影响的结果, 需要在未来的工作中进一步 source of precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Cli‐
mate, 30(5): 1807-1819. DOI: 10. 1175/jcli-d-15-0842. 1.
深入研究。
Zhang F M, Wang C H, Pu Z X, 2019. Genesis of Tibetan Plateau
参考文献: vortex: Roles of surface diabatic and atmospheric condensational
latent heating[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatolo‐
Cui Y, Wang C H, 2009. Comparison of sensible and latent heat flux‐ gy, 58(12): 2633-2651. DOI: 10. 1175/JAMC-D-19-0103. 1.
es during the transition season over the western Tibetan Plateau Zhang Q, Wu G X, Qian Y F, 2002. The bimodality of the 100 hPa
from reanalysis datasets[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 19(6): South Asia High and its relationship to the climate anomaly over
719-726. DOI: 10. 1016/j. pnsc. 2008. 11. 001. East Asia in summer[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of
Dong W H, Lin Y L, Wright J S, et al, 2016. Summer rainfall over Japan, 80(4): 733-744. DOI: 10. 2151/jmsj. 80. 733.
the southwestern Tibetan Plateau controlled by deep convection Zhang W X, Zhou T J, Zhang L X, 2017. Wetting and greening Tibet‐
over the Indian subcontinent[J]. Nature Communications, 7: 19. an Plateau in early summer in recent decades[J]. Journal of Geo‐
DOI: 10. 1038/ncomms10925. physical Research, 122(11): 5808-5822. DOI: 10. 1002/
Gao Y H, Guo L, Zhang Y X, 2014. Changes in moisture flux over 2017JD026468.
the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2011 and possible mechanisms 岑思弦, 陈文, 胡鹏, 等, 2021. 南亚高压演变过程及其变异机制研
[J]. Journal of Climate, 27(5): 1876-1893. DOI: 10. 1175/ 究进展[J]. 高原气象, 40(6): 1304-1317. DOI: 10. 7522/j.
JCLI-D-13-00321. 1. issn. 1000-0534. 2021. zk014.