Page 30 - 《高原气象》2022年第6期
P. 30
6 期 曹言超等:青藏高原春季积雪对北半球夏季季节内振荡的影响 1393
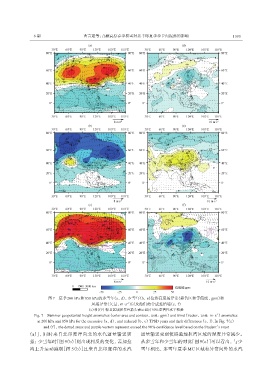
图7 夏季200 hPa和850 hPa的多雪年(a,d),少雪年(b,e)位势高度场异常(彩色区和等值线,gpm)和
-1
风场异常(矢量,m·s )以及他们的合成差值场(c,f)
(c)和(f)中标点区域和紫色箭头表示通过90%显著性水平检验
-1
Fig. 7 Summer geopotential height anomalies(color area and contour,unit:gpm)and wind(vector,unit:m·s )anomalies
at 200 hPa and 850 hPa for the excessive(a,d),and reduced(b,e)TPSD years and their differences(c,f). In Fig. 7(c)
and(f),the dotted areas and purple vectors represent exceed the 90% confidence level based on the Student’s t-test
(a)],同时来自北印度洋向北的水汽通量输送更 通量输送变弱使得孟加拉湾区域的湿度异常减少。
强;少雪年时[图 9(b)]则出现相反的变化,孟加拉 从多雪年和少雪年的对比[图 9(c)]可以看出,与少
湾上升运动减弱[图 5(b)]且来自北印度洋的水汽 雪年相比,多雪年夏季 MC 区域有异常向外的水汽