Page 226 - 《高原气象》2021年第5期
P. 226
5 期 王宏斌等:江苏不同等级雾的宏观和微观特征 1187
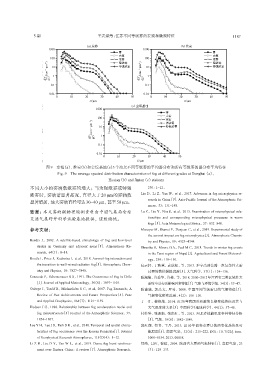
图9 东海(a)、淮安(b)和金坛基地(c)3个站点不同等级雾的平均谱分布和所有等级雾的谱分布平均特征
Fig. 9 The average spectral distribution characteristics of fog at different grades at Donghai(a),
Huaian(b)and Jintan(c)stations
不同大小的雾滴数浓雾均增大;当为强浓雾或特强 230:1-12,
浓雾时,雾滴谱显著拓宽,直径大于20 μm的雾滴数 Liu D,Li Z,Yan W,et al,2017. Advances in fog microphysics re‐
search in China[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of the Atmospheric Sci‐
显著增加,最大雾滴直径可达30~40 μm,甚至50 μm。
ences,53:131-148.
致谢:本文雾的微物理观测资料由中国气象局金坛 Lu C,Liu Y,Niu S,et al,2013. Examination of microphysical rela‐
交通气象野外科学试验基地提供,谨致谢忱。 tionships and corresponding microphysical processes in warm
fogs[J]. Acta Meteorological Sinica,27:832-848.
参考文献: Mazoyer M,Burnet F,Denjean C,et al,2019. Experimental study of
the aerosol impact on fog microphysics[J]. Atmospheric Chemis‐
Bendix J,2002. A satellite-based climatology of fog and low-level try and Physics,19:4323-4344.
stratus in Germany and adjacent areas[J]. Atmospheric Re‐ Shrestha S,Moore G A,Peel M C,2018. Trends in winter fog events
search,64(1):0-18. in the Terai region of Nepal[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorol‐
Boutle I,Price J,Kudzotsa I,et al,2018. Aerosol-fog interaction and ogy,259:118-130.
the transition to well-mixed radiation fog[J]. Atmospheric Chem‐ 包云轩,丁秋冀,袁成松,等,2013. 沪宁高速公路一次复杂性大雾
istry and Physics,18:7827-7840. 过程的数值模拟试验[J]. 大气科学,37(1):124-136.
Cereceda P,Schemenauer R S,1991. The Occurrence of Fog in Chile 陈翔翔,许爱华,许彬,等,2018. 2000-2012年江西省三类区域性大
[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology,30(8):1097-1105. 雾时空分布及影响因素特征[J]. 气象与环境学报,34(3):37-47.
Gultepe I,Tardif R,Michaelides S C,et al,2007. Fog Research:A 陈潇潇,郭品文,罗勇,2008. 中国不同等级雾日的气候特征[J].
Review of Past Achievements and Future Perspectives[J]. Pure 气候变化研究进展,4(2):106-110.
and Applied Geophysics,164(7):1121-1159. 丁一汇,柳艳菊,2014. 近 50 年我国雾和霾的长期变化特征及其与
Hudson J G,1980. Relationship between fog condensation nuclei and 大气湿度的关系[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),44(1):37-48.
fog microstructure[J]Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences,37: 付桂琴,张迎新,张庆红,等,2013. 河北省低能见度事件特征分析
1854-1867. [J]. 气象,39(8):1042-1049.
Lee Y H,Lee J S,Park S K,et al,2010. Temporal and spatial charac‐ 高红燕,贺音,王丹,2013. 近 50 年西安市雾日数的变化趋势及可
teristics of fog occurrence over the Korean Peninsula[J]. Journal 能原因[J]. 高原气象,32(6):215-222. DOI:10. 7522/j. issn.
of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,115(D14):1-12. 1000-0534. 2013. 00058.
Li Z H,Liu D Y,Yan W L,et al,2019. Dense fog burst reinforce‐ 贺皓,吕红,徐虹,2004. 陕西省大雾的气候特征[J]. 高原气象,23
ment over Eastern China:A review[J]. Atmospheric Research, (3):129-133.