Page 205 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第6期
P. 205
990 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 41 卷
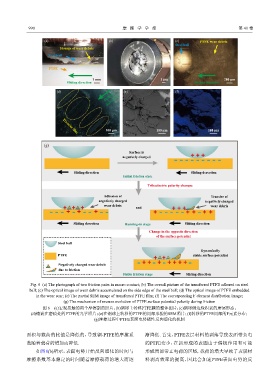
(a) (b) (c) PTFE wear debris
Steel ball
Storage of wear debris
Steel ball
PTFE
1 mm 1 μm 200 μm
Sliding direction Sliding direction
(d) (e) (f)
Sliding
direction
100 μm 100 μm 100 μm
Transfer film
(g)
Surface is
negatively charged
Sliding direction Sliding derection
Initial friction state
Triboelectric polarity changes
Adhesion of Transfer of
negatively charged negatively charged
wear debris wear debris
and
Sliding derection Running-in stage Sliding direction
Change in the opposite direction
of the surface potential
Steel ball
Dynamically
PTFE stable surface potential
Negatively charged wear debris
due to friction
Stable friction stage Sliding direction
Fig. 6 (a) The photograph of two friction pairs in macro contact; (b) The overall picture of the transferred PTFE adhered on steel
ball; (c) The optical image of wear debris accumulated on the side edge of the steel ball; (d) The optical image of PTFE embedded
in the wear scar; (e) The partial SEM image of transferred PTFE film; (f) The corresponding F element distribution image;
(g) The mechanism of reverse evolution of PTFE surface potential polarity during friction
图 6 (a)宏观接触的两个摩擦副的照片;(b)钢球上转移PTFE膜的整体图片;(c)钢球侧边缘积累的磨屑形态;
(d)镶嵌在磨痕处的PTFE的光学照片;(e)在钢球上转移的PTFE的局部形貌的SEM照片;(f)转移的PTFE局部的F元素分布;
(g)摩擦过程中PTFE表面电势极性反向演化的机制
面积与载荷的比值是降低的,导致钢-PTFE的摩擦系 渐降低. 首先,PTFE表层材料的剥落导致表面带负电
数随着载荷的增加而降低. 的PTFE变少,在新形成的表面由于偶极作用有可能
如图8(b)所示,表面电势开始反向演化的时间与 形成局部带正电荷的区域. 载荷的增大导致了表层材
摩擦系数基本稳定的时间随着摩擦载荷的增大而逐 料剥离效率的提高,因此会加速PTFE表面电势的反