Page 23 - 《软件学报》2025年第7期
P. 23
2944 软件学报 2025 年第 36 卷第 7 期
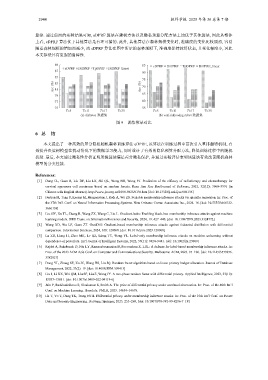
算法. 通过前面的实验结果可知, eDPRF 算法在建树方法以及隐私预算分配方法上均优于其他算法, 因此从整体
上看, eDPRF 算法优于其他算法是有理可循的. 此外, 其他算法在森林规模变化时, 准确度的变化比较剧烈, 容易
随着森林规模的增加而减少, 而 eDPRF 算法在图中所示的森林规模下, 准确度保持较好状态, 且变化幅度小, 因此
本文算法具有更强的鲁棒性.
89 85 eDPRF DiffPRF TpDPRF DiffPRF_linear
eDPRF DiffPRF TpDPRF DiffPRF_linear
87
80
85
75
Acc (%) 83 Acc (%) 70
81
65
79
77 60
75 55
T=5 T=11 T=17 T=35 T=5 T=11 T=17 T=35
(a) diabetes 数据集 (b) wall-following robot 数据集
图 9 训练算法对比
6 总 结
本文提出了一种高效的差分隐私随机森林训练算法 eDPRF, 该算法在训练过程中首次引入重排翻转机制, 有
效提升决策树模型在扰动情况下的数据学习能力, 同时设计了有效的隐私预算分配方法, 降低训练过程中的随机
扰动. 最后, 本文通过隐私性分析证明所提算法满足差分隐私保护, 并通过实验评估表明该算法有效改善随机森林
模型的分类性能.
References:
[1] Deng CL, Guan B, Liu DF, Liu LX, Shi QL, Wang HR, Wang YJ. Prediction of the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy for
cervical squamous cell carcinoma based on random forests. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/Journal of Software, 2021, 32(12): 3960–3976 (in
Chinese with English abstract). http://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/6136.htm [doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006136]
[2] Bertran M, Tang S, Kearns M, Morgenstern J, Roth A, Wu ZS. Scalable membership inference attacks via quantile regression. In: Proc. of
the 37th Int’l Conf. on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. 16. [doi: 10.5555/3666122.
3666138]
[3] Liu GY, Xu TL, Zhang R, Wang ZX, Wang C, Liu L. Gradient-leaks: Enabling black-box membership inference attacks against machine
learning models. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 427–440. [doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3324772]
[4] Wang XD, Wu LF, Guan ZT. GradDiff: Gradient-based membership inference attacks against federated distillation with differential
comparison. Information Sciences, 2024, 658: 120068. [doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.120068]
[5] Lu ZB, Liang H, Zhao MH, Lv QZ, Liang TC, Wang YL. Label-only membership inference attacks on machine unlearning without
dependence of posteriors. Int’l Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(11): 9424–9441. [doi: 10.1002/int.23000]
[6] Rajabi A, Sahabandu D, Niu LY, Ramasubramanian B, Poovendran R. LDL: A defense for label-based membership inference attacks. In:
Proc. of the 2023 ACM Asia Conf. on Computer and Communications Security. Melbourne: ACM, 2023. 95–108. [doi: 10.1145/3579856.
3582821]
[7] Dong YL, Zhang SF, Xu JC, Wang HS, Liu JQ. Random forest algorithm based on linear privacy budget allocation. Journal of Database
Management, 2022, 33(2): 19. [doi: 10.4018/JDM.309413]
[8] Liu J, Li XX, Wei QM, Liu SF, Liu Z, Wang JY. A two-phase random forest with differential privacy. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(10):
13037–13051. [doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-04119-6]
[9] Jain P, Raskhodnikova S, Sivakumar S, Smith A. The price of differential privacy under continual observation. In: Proc. of the 40th Int’l
Conf. on Machine Learning. Honolulu: PMLR, 2023. 14654–14678.
[10] Ha T, Vo T, Dang TK, Trang NTH. Differential privacy under membership inference attacks. In: Proc. of the 10th Int’l Conf. on Future
Data and Security Engineering. Da Nang: Springer, 2023. 255–269. [doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-8296-7_18]