Page 145 - 《软件学报》2021年第5期
P. 145
王晓峰 等:可满足性问题中信念传播算法的收敛性分析 1369
1
n=120
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
谱半径 ρ 0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
约束参数α=m/n
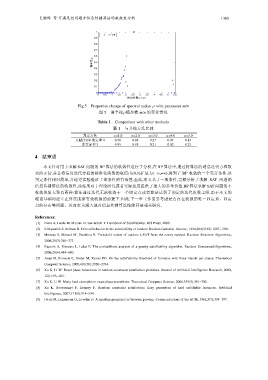
Fig.5 Properties change of spectral radius ρ with parameter m/n
图 5 谱半径ρ随参数 m/n 的变化情况
Table 1 Comparison with other methods
表 1 与其他方法比较
判定方法 α =1.0 α =2.0 α =3.0 α =4.0 α =5.0
文献[53]中的定理 4 0.91 0.84 0.27 0.07 0.13
本文定理 3 0.95 0.88 0.21 0.02 0.22
4 结束语
本文针对用于求解 SAT 问题的 BP 算法的收敛性进行了分析,在 BP 算法中,通过将算法的消息迭代方程取
双曲正切,并且将信息迭代方程的标准化函数的取值由(0,1)扩展为(−∞,+∞),得到了 BP 收敛的一个充分条件,该
判定条件相对简单,并通过实验验证了该条件的有效性.至此,本文基于一般条件,完整分析了求解 SAT 问题的
信息传播算法的收敛性,该结果对于理论研究或者实际应用提供了很大的参考价值.BP 算法求解 SAT 问题的不
收敛现象大致有两种:算法通过迭代无法收敛于一个固定点或者算法达到了预定的迭代次数上限.由于本文的
理论基础均建立在算法能够有效收敛的前提下.因此,下一步工作需要考虑是否存在收敛的唯一固定点、固定
点的分布等问题、从而更为深入地对信息传播算法性能开展相关研究.
References:
[1] Biere A, Heule M, Maaren H. van Walsh T. Handbook of Satisfiability. IOS Press, 2009.
[2] Kirkpatrick S, Selman B. Critical behavior in the satisfiability of random Boolean formulae. Science, 1994,264(5163):1297−1301.
[3] Mertens S, Mezard M, Zecchina R. Threshold values of random k-SAT from the cavity method. Random Structure Algorithms,
2006,28(3):340−373.
[4] Kaporis A, Kirousis L, Lalas E. The probabilistic analysis of a greedy satisfiability algorithm. Random Structures&Algorithms,
2006,28(4):444−480.
[5] Josep D, Kirousis L, Dieter M, Xavier PG. On the satisfiability threshold of formulas with three literals per clause. Theoretical
Computer Science, 2009,410(30):2920−2934.
[6] Xu K, Li W. Exact phase transitions in random constraint satisfaction problems. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2000,
12(1):93−103.
[7] Xu K, Li W. Many hard examples in exact phase transitions. Theoretical Computer Science, 2006,355(3):291−302.
[8] Xu K, Boussemart F, Hemery F. Random constraint satisfaction: Easy generation of hard satisfiable instances. Artificial
Intelligence, 2007,171(8):514−534.
[9] Davis M, Logemann G, Lovelan D. A machine program f or theorem proving. Communications of the ACM, 1962,5(7):394−397.