Page 85 - 《摩擦学学报》2021年第4期
P. 85
528 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 41 卷
1.0
(a) 0.86 (b) 25 ℃
3 000 2 738
25 ℃ 2 545 50 ℃
0.8 80 ℃
50 ℃ 0.56 0.68 0.64 2 500 660
Friction coefficient 0.6 0.51 Wear volume loss/(10 −5 mm 3 ) 500 266 315
80 ℃
0.4
0.2 0.13 0.12 250 113 139
0.1
20
0.0 0
Pure water Pure water
PTFE@SiO 2 PTFE/SiO 2 PTFE@SiO 2 PTFE/SiO 2
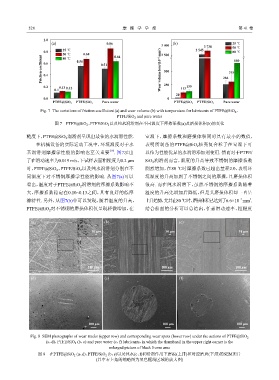
Fig. 7 The variations of friction coefficient (a) and wear volume (b) with temperature for lubricants of PTFE@SiO 2 ,
PTFE/SiO 2 and pure water
图 7 PTFE@SiO 2 、PTFE/SiO 2 以及纯水润滑剂在不同温度下摩擦系数(a)及磨损体积(b)的变化
糙度下,PTFE@SiO 润滑剂呈现出最佳的水润滑性能. 室温下,摩擦系数和磨损体积同时具有最小的数值,
2
在机械设备的实际运动工况中,环境温度对于水 表明所制备的PTFE@SiO 核壳复合粒子在室温下可
2
[19]
基润滑剂摩擦学性能的影响也至关重要 . 图7示出 以作为性能优异的水润滑添加剂使用. 然而对于PTFE/
了在滑动速率为0.019 m/s、下试样表面粗糙度为0.2 μm SiO 润滑剂而言,温度的升高导致不锈钢的摩擦系数
2
时,PTFE@SiO 、PTFE/SiO 以及纯水润滑剂分别在不 剧烈增加,在80 ℃时摩擦系数已超出量程2.0,表明环
2
2
同温度下对不锈钢摩擦学性能的影响. 从图7(a)可以 境温度的升高加剧了不锈钢之间的摩擦,且磨损体积
看出,温度对于PTFE@SiO 润滑剂的摩擦系数影响不 很高. 而在纯水润滑下,虽然不锈钢的摩擦系数随着
2
大,摩擦系数稳定在0.10~0.13之间,具有良好的低摩 温度的升高先增加后降低,但是其磨损体积却一直呈
擦特性. 另外,从图7(b)中可以发现,随着温度的升高, 上升趋势,尤其在80 ℃时,磨损体积已达到了6.6×10 mm .
−3
3
PTFE@SiO 对不锈钢的磨损体积仅呈现轻微增加,在 结合前面的分析可以总结出,任意滑动速率、粗糙度
2
(a) (b) (c)
10 μm 10 μm 10 μm
100 μm 100 μm 100 μm
(d) (e) (f)
100 μm 100 μm 100 μm
Fig. 8 SEM photographs of wear tracks (upper row) and corresponding wear spots (lower row) under the actions of PTFE@SiO 2
(a,d),PTFE/SiO 2 (b,e) and pure water (c,f) lubricants,in which the thumbnail in the upper right corner is the
enlarged picture of black frame area
图 8 在PTFE@SiO 2 (a、d)、PTFE/SiO 2 (b、e)以及纯水(c、f)润滑剂作用下磨痕(上排)和对应磨斑(下排)的SEM照片
(其中右上角的缩略图为黑色框线区域的放大图)