Page 188 - 《高原气象》2022年第6期
P. 188
6 期 陈泽霞等:基于CMIP6多模式的黑河干流山区降水气温变化趋势分析 1551
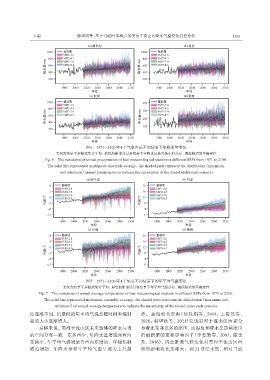
图6 1971-2100年4个气象台站不同情景下年降水量变化
实线为情景下多模式集合平均;彩色阴影部分是各情景下年降水量最大最小值分布,表征模式的不确定性
Fig. 6 The variations of annual precipitation of four meteorological stations in different SSPs from 1971 to 2100.
The solid line represented multimode ensemble average,the shaded parts represent the distribution(maximum
and minimum)annual precipitation to indicate the uncertainty of the model under each scenario
图7 1971-2100年4个站点不同情景下的年平均气温变化
实线为情景下多模式集合平均;彩色阴影部分是各情景下年平均气温分布,表征模式的不确定性
Fig. 7 The variations of annual average temperature of four meteorological stations in different SSPs from 1971 to 2100.
The solid line represented multimode ensemble average,the shaded parts represent the distribution(maximum and
minimum)of annual average temperature to indicate the uncertainty of the model under each scenario
度逐渐不同,情景间的年平均气温差随时间和辐射 势。查阅相关资料(怀保娟等,2014;王俊瑶等,
强迫大小逐渐增大。 2020;赵华秋等,2021)发现黑河干流山区西部分
总体来说,黑河干流山区未来整体的降水与当 布着比东部更多的冰川,而温度和降水是影响冰川
前空间分布一致—东多西少,年降水量增速自西向 消融积累的重要影响因子(李忠勤等,2003;陈忠
东减小,年平均气温增量自西向东增加。伴随辐射 升,2016),因此推测气候变化对黑河干流山区西
强迫增加,年降水量和年平均气温呈现为上升趋 部的影响将比东部大。到 21 世纪末期,相对当前