Page 151 - 《软件学报》2024年第4期
P. 151
闫涛 等: 一种分组并行的轻量化实时微观三维形貌重建方法 1729
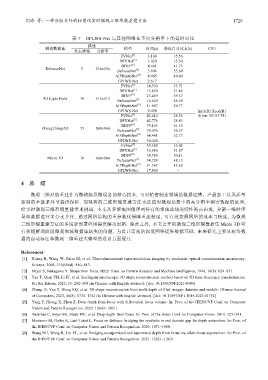
表 7 GPLWS-Net 与其他网络在不同分辨率下的延时对比
描述
测试数据集 模型 时间(s) 降低百分比↓(%) CPU
焦点堆栈 分辨率
[5]
FVNet 3.100 15.56
[5]
DFVNet 3.020 13.34
[6]
DDFF 4.491 41.73
DefocusNet 5 256×256 [7]
DefocusNet 5.906 55.69
[8]
AiFDepthNet 4.405 40.60
GPLWS-Net 2.617 −
FVNet 14.330 33.71
[5]
[5]
DFVNet 13.850 31.42
[6]
DDFF 23.489 59.57
4D Light Field 10 512×512 DefocusNet 18.624 46.59
[7]
[8]
AiFDepthNet 11.987 20.77
GPLWS-Net 9.498 − Intel(R) Xeon(R)
[5]
FVNet 42.614 28.56 Silver 4210 CPU
[5]
DFVNet 42.776 28.83
[6]
DDFF 79.165 61.55
FlyingThings3D 15 540×960 DefocusNet 70.076 56.57
[7]
[8]
AiFDepthNet 64.441 52.77
GPLWS-Net 30.440 −
[5]
FVNet 39.580 55.02
[5]
DFVNet 36.980 51.87
[6]
DDFF 38.780 54.11
Micro 3D 10 600×800 [7]
DefocusNet 34.328 48.15
[8]
AiFDepthNet 31.567 43.62
GPLWS-Net 17.800 −
4 总 结
微观三维形貌重建作为微纳级显微设备的核心技术, 可对精密制造领域的数据建模、产品加工以及质量
控制的全链条环节提供保障. 而现有的三维形貌重建方法无法应对微观场景中的高分辨率稠密数据的处理,
给实时微观三维形貌重建带来挑战. 本文从多聚焦图像序列特有的聚焦曲线连续性特点出发, 分割一维时序
景深数据进行多分支并行, 通过网络结构的重参数化保障重建精度, 可有效兼顾网络的效率与精度, 为微观
三维形貌重建方法的多场景部署应用提供解决思路. 除此之外, 本文公开的微观三维形貌数据集 Micro 3D 可
有效缓解现阶段微观领域数据集缺失的问题, 为设计高效的深度网络提供数据基础. 未来研究主要从标签数
据的自动标注和微观三维重建大模型的设计方面展开.
References:
[1] Huang B, Wang W, Bates M, et al. Three-dimensional super-resolution imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy.
Science, 2008, 319(5864): 810−813.
[2] Nayar S, Nakagawa Y. Shape from focus. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1994, 16(8): 824−831.
[3] Yan T, Qian YH, Li FJ, et al. Intelligent microscopic 3D shape reconstruction method based on 3D time-frequency transformation.
Sci Sin Inform, 2023, 53: 282−308 (in Chinese with English abstract). [doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0386]
[4] Zhang JF, Yan T, Wang KQ, et al. 3D shape reconstruction from multi depth of filed images: datasets and models. Chinese Journal
of Computers, 2023, 46(8): 1734−1752 (in Chinese with English abstract). [doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01734]
[5] Yang F, Huang X, Zhou Z. Deep depth from focus with differential focus volume. In: Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2022. 12642−12651.
[6] Hazirbas C, Soyer SG, Staab MC, et al. Deep depth from focus. In: Proc. of the Asian Conf. on Computer Vision. 2018. 525−541.
[7] Maximov M, Galim K, Leal-Taixé L. Focus on defocus: bridging the synthetic to real domain gap for depth estimation. In: Proc. of
the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020. 1071−1080.
[8] Wang NH, Wang R, Liu YL, et al. Bridging unsupervised and supervised depth from focus via all-in-focus supervision. In: Proc. of
the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2021. 12621−12631.