Page 136 - 《软件学报》2024年第4期
P. 136
1714 软件学报 2024 年第 35 卷第 4 期
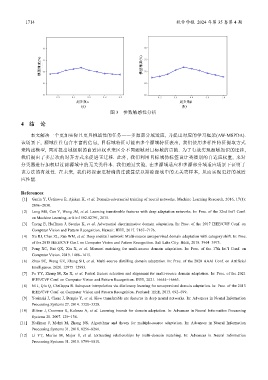
模型精度(%) 模型精度(%)
超参数α 超参数β
(a) (b)
图 3 参数敏感性分析
4 结 论
本文解决一个更加实际且更具挑战性的任务——多源部分域适应, 并提出对应的学习框架(AW-MSPDA).
该场景下, 源域往往包含丰富的信息, 目标域特征可能由多个源域特征表出, 我们使用多样性特征提取方式
来构建模型, 同时提出域级别的自适应权重来区分不同源域对目标域的贡献. 为了有效实现源域知识的迁移,
我们提出了多层次的对齐方式来促进正迁移. 此外, 我们利用目标域伪标签设计类级别的自适应权重, 来对
分类器进行加权以过滤源域中的无关类样本. 我们通过实验, 在多源域适应和多源部分域适应场景下证明了
该方法的有效性. 在未来, 我们将探索更精确的过滤算法以排除源域中的无关类样本, 从而实现更好的域适
应性能.
References:
[1] Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1):
2096−2030.
[2] Long MS, Cao Y, Wang JM, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proc. of the 32nd Int’l Conf.
on Machine Learning. arXiv:1502.02791, 2015.
[3] Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Saenko K, et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proc. of the 2017 IEEE/CVF Conf. on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii: IEEE, 2017. 7167−7176.
[4] Xu RJ, Chen ZL, Zuo WM, et al. Deep cocktail network: Multi-source unsupervised domain adaptation with category shift. In: Proc.
of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018. 3964−3973.
[5] Peng XC, Bai QX, Xia X, et al. Moment matching for multi-source domain adaptation. In: Proc. of the 17th Int’l Conf. on
Computer Vision. 2019. 1406−1415.
[6] Zhao SC, Wang GZ, Zhang SH, et al. Multi-source distilling domain adaptation. In: Proc. of the 2020 AAAI Conf. on Artificial
Intelligence. 2020. 12975−12983.
[7] Fu YY, Zhang M, Xu X, et al. Partial feature selection and alignment for multi-source domain adaptation. In: Proc. of the 2021
IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2021. 16654−16663.
[8] Ni J, Qiu Q, Chellappa R. Subspace interpolation via dictionary learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proc. of the 2013
IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland: IEEE, 2013. 692−699.
[9] Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 27. 2014. 3320−3328.
[10] Blitzer J, Crammer K, Kulesza A, et al. Learning bounds for domain adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems 20. 2007. 129−136.
[11] Hoffman J, Mohri M, Zhang NS. Algorithms and theory for multiple-source adaptation. In: Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 31. 2018. 8256−8266.
[12] Li YT, Murias M, Major S, et al. Extracting relationships by multi-domain matching. In: Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems 31. 2018. 6799−6810.