Page 201 - 《软件学报》2021年第11期
P. 201
黄立峰 等:一种基于进化策略和注意力机制的黑盒对抗攻击算法 3527
该防御模型抵抗其他黑盒攻击(AutoZOOM、QL-attack)的能力.
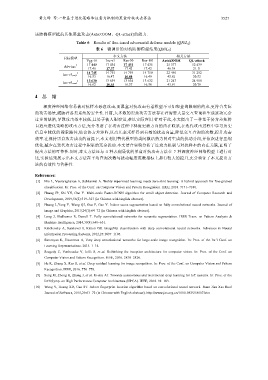
Table 6 Results of fine-tuned adversarial defense models (QN/L 2 )
表 6 微调后的对抗防御模型结果(QN/L 2 )
本文方法 相关方法
目标模型
Vgg-16 Inc-v3 Res-50 Res-101 AutoZOOM QL-attack
Adv-Inc * 17 440 17 434 17 431 17 435 25 377 52 439
17.46 17.37 17.42 17.42 46.39 21.11
Inc-v3 ens3 * 14 745 14 755 14 759 14 750 22 440 31 252
16.53 16.47 16.44 16.49 45.62 20.52
Inc-v3 ens4 * 13 630 13 639 13 634 13 632 21 247 24 980
16.58
43.91
20.79
16.62
16.55
16.57
4 总 结
深度神经网络容易被对抗样本恶意攻击,而黑盒对抗攻击有着模型不可知和查询限制的约束,更符合实际
的攻击场景,威胁着各类系统的安全性.目前,大多数的黑盒攻击方法存在着需要大量交互查询和生成扰动冗余
过多的缺陷,导致攻击效率较低,且易于被人眼察觉,难以实际应用.针对于此,本文提出了一种基于协方差矩阵
自适应进化策略的攻击方法,充分考虑了在攻击过程中梯度更新方向的内在联系,在迭代攻击过程中学习历史
信息中较优的搜索路径,结合协方差矩阵,以高几率采样得到有效的扰动向量,降低交互查询的次数,提升攻击
效率.在保持黑盒攻击成功的前提下,本文利用替代模型的类间激活热力图对生成的扰动分组,并依次进行压缩
优化,减少在迭代攻击过程中积累的冗余扰动.本文结合实验分析了注意力机制与对抗样本的内在关联,证明了
提出方法的可靠性.同时,本文方法还与 4 种表现最优的黑盒对抗攻击方法在 7 种深度神经网络模型上进行对
比,实验结果展示出本文方法在平均查询次数与扰动幅度范数指标上都有较大的提升,充分验证了本文提出方
法的有效性与鲁棒性.
References:
[1] Niu L, Veeraraghavan A, Sabharwal A. Webly supervised learning meets zero-shot learning: A hybrid approach for fine-grained
classification. In: Proc. of the Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2018. 7171−7180.
[2] Huang JP, Shi YH, Gao Y. Multi-scale Faster-RCNN algorithm for small object detection. Journal of Computer Research and
Development, 2019,56(2):319−327 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Huang L,Yang Y, Wang QJ, Guo F, Gao Y. Indoor scene segmentation based on fully convolutional neural networks. Journal of
Image and Graphics, 2019,24(1):64−72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis &
Machine Intelligence, 2014,39(4):640−651.
[5] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 2012,25:1097−1105.
[6] Simonyan K, Zisserman A, Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proc. of the Int’l Conf. on
Learning Representations. 2015. 1−14.
[7] Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proc. of the Conf. on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2016. 2818−2826.
[8] He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proc. of the Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition. IEEE, 2016. 770−778.
[9] Song M, Zhong K, Zhang J, et al. In-situ AI: Towards autonomous and incremental deep learning for IoT systems. In: Proc. of the
Int’l Symp. on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA). IEEE, 2018. 92−103.
[10] Wang Y, Huang XD, Guo ST. Indoor fingerprint location algorithm based on convolutional neural network. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/
Journal of Software, 2018,29:63−72 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/18007.htm