Page 107 - 摩擦学学报2025年第5期
P. 107
第 5 期 王任侠, 等: 闸片摩擦块尺寸设计对高速列车制动振动噪声的调控作用 741
Caliper
3D model
(Solid Works)
Fixture
Disc Finite element model
ABAQUS Static general analysis
Block Node contact Node sliding
stress distribution distance
(a)
UMESHMOTION +ALE Wear depth and
wear direction
Grid and node
F updating
Wear No
ω simulation
end?
Yes
F End output
results
(b) (c)
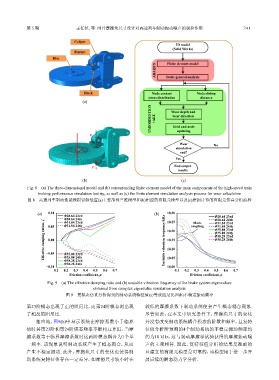
Fig. 8 (a) The three-dimensional model and (b) corresponding finite element model of the main components of the high-speed train
braking performance simulation test rig, as well as (c) the finite element simulation analysis process for wear calculation
图 8 高速列车制动性能模拟试验装置(a)主要部件三维模型和(b)相应的有限元模型以及(c)磨损计算的有限元仿真分析流程
(a) 0.10 Φ28.64 23rd (b) 18.30
Φ28.64 24th 18.25 coupling Φ28.64 23rd
Φ28.64 24th
Φ31.84 23rd
Effective damping ration, ζ 0.00 Unstable vibration frequency/kHz 18.20 Φ35.08 24th
Mode
Φ31.84 23rd
Φ31.84 24th
Φ31.84 24th
0.05
Φ35.08 23rd
Φ38.28 23rd
Φ38.28 24th
18.15
18.10
−0.05
Φ35.08 23rd
Φ35.08 24th
Φ38.28 23rd
Φ38.28 24th 18.05
−0.10 18.00
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
Friction coefficient, μ Friction coefficient, μ
Fig. 9 (a) The effective damping ratio and (b) unstable vibration frequency of the brake system eigenvalues
obtained from complex eigenvalue simulation analysis
图 9 复模态仿真分析得到的制动系统特征值(a)等效阻尼比和(b)不稳定振动频率
第23阶模态出现了正的阻尼比,而第24阶模态则出现 较低的摩擦系数下制动系统便会产生模态耦合现象.
了相反的阻尼比. 尽管如此,在本文中研究条件下,摩擦块尺寸的变化
相应地,图9(b)中显示系统在摩擦系数小于临界 并没有改变制动系统耦合模态的阶数和频率,且复特
值时其第23阶和第24阶模态频率不断相互靠近,当摩 征值分析所预测的4个制动系统的不稳定振动频率均
擦系数等于临界摩擦系数时这两阶模态耦合为1个单 约为18 kHz,这与制动摩擦学试验获得的摩擦振动噪
一频率. 该现象说明制动系统产生了模态耦合,从而 声的主频相符. 因此,复特征值分析的结果是准确的
产生不稳定振动. 此外,摩擦块尺寸的变化也使得制 且建立的有限元模型是可靠的,该模型用于进一步开
动系统复特征值存在一定差异,如摩擦尺寸较小时在 展后续的瞬态动力学分析.