Page 77 - 《摩擦学学报》2020年第5期
P. 77
632 摩 擦 学 学 报 第 40 卷
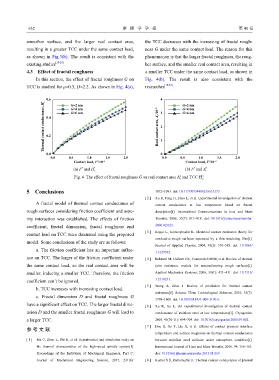
smoother surface, and the larger real contact area, the TCC decreases with the increasing of fractal rough-
resulting in a greater TCC under the same contact load, ness G under the same contact load. The reason for this
as shown in Fig.3(b). The result is consistent with the phenomenon is that the larger fractal roughness, the roug-
[18-20]
existing studies . her surface, and the smaller real contact area, resulting in
4.3 Effect of fractal roughness a smaller TCC under the same contact load, as shown in
In this section, the effect of fractal roughness G on Fig. 4(b). The result is also consistent with the
[18-20]
TCC is studied for μ=0.3, D=2.2. As shown in Fig. 4(a), researches .
0.6 G=2 nm 4 3 G=2 nm
c
Thermal contact conductance, H * 0.4 Real contact area, A * /10 −3 r 2 1
G=4 nm
G=4 nm
G=6 nm
G=6 nm
0.2
0.0 0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
Contact load, F /10 −4 Contact load, F /10 −4
*
*
* * * *
(a) F and H c (b) F and A r
∗
Fig. 4 The effect of fractal roughness G on real contact area A and TCC H ∗
r c
5 Conclusions 1072–1093. doi: 10.1177/0954406216631573.
[ 2 ] Xu R, Feng H, Zhao L, et al. Experimental investigation of thermal
A fractal model of thermal contact conductance of
contact conductance at low temperature based on fractal
rough surfaces considering friction coefficient and aspe- description[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass
rity interaction was established. The effects of friction Transfer, 2006, 33(7): 811–818. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.
coefficient, fractal dimension, fractal roughness and 2006.02.023.
[ 3 ] Kogut L, Komvopoulos K. Electrical contact resistance theory for
contact load on TCC were discussed using the proposed
conductive rough surfaces separated by a thin insulating film[J].
model. Some conclusions of the study are as follows:
Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 95(2): 576–585. doi: 10.1063/
a. The friction coefficient has an important influe-
1.1629392.
nce on TCC. The larger of the friction coefficient under [ 4 ] Bahrami M, Culham J R, Yananovich M M, et al. Review of thermal
the same contact load, so the real contact area will be joint resistance models for nonconforming rough surfaces[J].
smaller, inducing a smaller TCC. Therefore, the friction Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2006, 59(1): 411–431. doi: 10.1115/
1.2110231.
coefficient can’t be ignored.
[ 5 ] Wang A, Zhao J. Review of prediction for thermal contact
b. TCC increases with increasing contact load.
resistance[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2010, 53(7):
c. Fractal dimension D and fractal roughness G
1798–1808. doi: 10.1007/s11431-009-3190-6.
have a significant effect on TCC. The larger fractal dime- [ 6 ] Xu R, Xu L. An experimental investigation of thermal contact
nsion D and the smaller fractal roughness G will lead to conductance of stainless steel at low temperatures[J]. Cryogenics,
a larger TCC. 2005, 45(10-11): 694–704. doi: 10.1016/j.cryogenics.2005.09.002.
[ 7 ] Dou R, Ge T, Liu X, et al. Effects of contact pressure interface
参 考 文 献
temperature and surface roughness on thermal contact conductance
[ 1 ] Ma C, Zhao L, Shi H, et al. Experimental and simulation study on between stainless steel surfaces under atmosphere condition[J].
the thermal characteristics of the high-speed spindle system[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 94: 156–163.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.11.069.
Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2017, 231(6): [ 8 ] Kumar S S, Ramamurthi K. Thermal contact conductance of pressed