Page 57 - 《高原气象》2022年第5期
P. 57
高 原 气 象 41 卷
1150
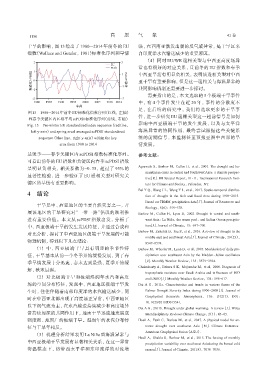
干旱的影响,图 13 给出了 1980-2014 年前冬的 EU 强,在西南亚激发出暖的反气旋异常,是干旱区来
指数(Wallace and Gutzler,1981)标准化序列和旱情 自印度洋水汽输送减少的重要原因。
(4) 同时 EU/WR 遥相关型与中西亚高度场异
常也有很好的对应关系,且前冬的 EU 指数和春季
中西亚旱情有明显负相关,表明该遥相关型对中西
亚干旱有重要影响,但是这一遥相关与海温异常的
共同影响机制还需要进一步探讨。
需要指出的是,本文选取的 5 个极端干旱事件
中,有 4 个事件发生在近 20 年,事件的分散度不
足,在后续的研究中,我们将选取更多的干旱事
图13 1980-2014年前冬EU标准化指数序列(红线,左轴)
件,进一步研究 EU 遥相关型这一超前信号是如何
和春季关键区内区域平均scPDSI标准化序列(蓝线,右轴)
Fig. 13 Pre-winter EU standardized index sequence(red line, 影响中西亚极端干旱的发生发展,以及与太平洋
left y-axis)and spring areal averaged scPDSI standardized 海温异常的协同作用,最终尝试根据这些关键系
sequence(blue line,right y-axis)within the key 统的前期信号,来监测甚至预报亚洲中西部的旱
area from 1980 to 2014 情发展。
最强季——春季关键区内 scPDSI指数标准化序列。 参考文献:
可看出前冬的 EU指数和关键区内春季 scPDSI指数
呈明显负相关,相关系数为-0. 35,超过了 95% 的 Agrawala S,Barlow M,Cullen H,et al,2001. The drought and hu‐
manitarian crisis in central and Southwest Asia:a climate perspec‐
显著性检验,进一步验证了 EU 遥相关型对研究关
tive[R]. IRI Special Report,01‐11,International Research Insti‐
键区的旱情有重要影响。 tute for Climate and Society,Palisades,NY.
Bai Y Q,Wang J L,Wang Y J,et al,2017. Spatio‐temporal distribu‐
4 结论 tion of drought in the Belt and Road Area during 1998-2015.
Based on TRMM precipitation data[J]. Journal of Resources and
干旱是中、西亚地区的主要自然灾害之一,开
Ecology,8(6):559-570.
展该地区的干旱研究对“一带一路”倡议的顺利推 Barlow M,Cullen H,Lyon B,2002. Drought in central and south‐
进有重要价值。本文从 scPDSI 指数出发,分析了 west Asia:La Niña,the warm pool,and Indian Ocean precipita‐
中、西亚极端干旱的发生发展特征,并通过合成和 tion[J]. Journal of Climate,15:697-700.
Barlow M,Zaitchik B,Paz S,et al,2016. A review of drought in the
对比分析,探讨了中西亚地区极端干旱发展的可能
middle east and southwest Asia[J]. Journal of Climate,29(23),
物理机制,得到以下几点结论: 8547-8574.
(1) 中、西亚极端干旱具有明显的季节性特 Barlow M,Wheeler M,Lyon B,et al,2005. Modulation of daily pre‐
征,干旱基本从前一个冬季开始缓慢发展,到了春 cipitation over southwest Asia by the Madden ‐ Julian oscillation
季旱情发展十分迅速,春末达到最强,夏季开始缓 [J]. Monthly Weather Review,133:3579-3594.
Chakraborty A,Behera S K,Mujumdar M,et al,2006. Diagnosis of
解,秋末最弱。
tropospheric moisture over Saudi Arabia and in fl uences of IOD
(2) 对比极端干旱和极端湿润年水汽和高度 and ENSO[J]. Monthly Weather Review,134:598-617.
场的空间分布特征,发现中、西亚地区极端干旱发 Dai A G,2011a. Characteristics and trends in various forms of the
生时,往往伴随着南部印度洋的水汽输送减少,同 Palmer Drought Severity Index during 1900-2008[J]. Journal of
Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 116: D12115. DOI:
时在中西亚北部出现了高度场正异常,中西亚地区
10. 1029/2010JD015541.
以下沉气流为主,在水汽输送持续减少和高度场异
Dai A G,2011b. Drought under global warming:A review[J]. Wiley
常持续加深的共同作用下,地面干旱迅速地发展成 Interdisciplinary Reviews Climate Change,2(1):45-65.
强度强、范围广的极端干旱。湿润年的水汽分布特 Hoell A,Funk C,Barlow M,et al,2017. A physical model for ex‐
征与干旱年相反。 treme drought over southwest Asia [M]. Climate Extremes.
American Geophysical Union(AGU).
(3) 机理分析结果表明 La Niña 型海温异常与
Hoell A,Shukla S,Barlow M,et al,2015. The forcing of monthly
中西亚极端干旱发展有显著相关关系,在这一异常 precipitation variability over southwest Asiaduring the boreal cold
海温模态下,热带西太平洋和东印度洋的对流增 season[J]. Journal of Climate,28(18),7038-7056.