Page 255 - 《软件学报》2020年第12期
P. 255
任艳丽 等:可修改的区块链方案 3921
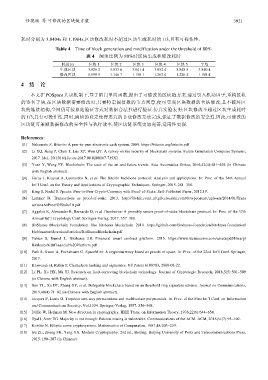
耗时分别为 3.8404s 和 1.1984s,区块修改耗时不超过区块生成耗时的 1/3,具有可操作性.
Table 4 Time of block generation and modification under the threshold of 80%
表 4 阈值比例为 80%时区块生成和修改耗时
耗时(s) 区块 1 区块 2 区块 3 区块 4 区块 5 平均
生成区块 3.826 2 3.833 6 3.841 4 3.852 4 3.848 5 3.840 4
修改区块 1.198 5 1.146 7 1.158 1 1.262 4 1.226 4 1.198 4
4 结 论
本文在 POSpace 共识机制下,基于陷门单向函数,提出了可修改的区块链方案.通过引入机动因子,重构区块
的签名子块,在区块数据需要修改时,只要特定阈值数的节点同意,便可实现区块数据的合法修改,且不破坏区
块的链接结构,全网仍可按原始验证方式对数据合法性进行验证.仿真实验表明:区块修改不超过区块生成耗时
的 1/3,具有可操作性.同时,阈值的设定使得恶意的非法修改无法完成,保证了数据修改的安全性.因此,可修改的
区块链可兼顾数据修改的安全性与执行效率,使区块链系统更加完善,适用性更强.
References:
[1] Nakamoto S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. 2009. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
[2] Li XQ, Jiang P, Chen T, Luo XP, Wen QY. A survey on the security of blockchain systems. Future Generation Computer Systems,
2017. [doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.08.0200167-739X]
[3] Yuan Y, Wang FY. Blockchain: The state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016,42(4):481−494 (in Chinese
with English abstract).
[4] Garay J, Kiayias A, Leonardos N, et al. The Bitcoin backbone protocol: Analysis and applications. In: Proc. of the 34th Annual
Int’l Conf. on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Springer, 2015. 281−310.
[5] King S, Nadal S. Ppcoin: Peer-to-Peer Crypto-Currency with Proof-of-Stake. Self-Published Paper, 2012.19.
[6] Larimer D. Transactions as proof-of-stake. 2013. http://7fvhfe.com1.z0.glb.clouddn.com/@/wpcontent/uploads/2014/01/Trans
actionsAsProofOfStake10.pdf
[7] Aggelos K, Alexander R, Bernardo D, et al. Ouroboros: A provably secure proof-of-stake blockchain protocol. In: Proc. of the 37th
Annual Int’l Cryptology Conf. Springer-Verlag, 2017. 357−388.
[8] BitShares Blockchain Foundation. The bitshares blockchain. 2014. https://github.com/bitshares-foundation/bitshares.foundation/
blob/master/download/articles/BitSharesBlockchain.pdf
[9] Fabian S, Daniel L. Bitshares 2.0: Financial smart contract platform. 2015. https://www.weusecoins.com/assets/pdf/library/
Bitshares%20Financial%20Platform.pdf
[10] Park S, Kwon A, Fuchsbauer G. SpaceMint: A cryptocurrency based on proofs of space. In: Proc. of the 22nd Int’l Conf. Springer,
2017.
[11] Krawczyk H, Rabin T. Chameleon hashing and signatures. US Patent 6108783, 2000-08-22.
[12] Li PL, Xu HX, Ma TJ. Research on fault-correcting blockchain technology. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2018,5(5):501−509
(in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Ren YL, Xu DT, Zhang XP, et al. Delegable blockchain based on an threshold ring signature scheme. Journal on Communications,
2019,40(4):71−82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Jacques P, Louis G. Trapdoor one-way permutations and multivariate polynomials. In: Proc. of the First Int’l Conf. on Information
and Communications Security, Vol.1334. Springer-Verlag, 1997. 356−368.
[15] Diffie W, Hellman M. New direction in cryptography. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory, 1976,22(6):644−654.
[16] Eyal I, Sirer EG. Majority is not enough: Bitcoin mining is vulnerable. Communications of the ACM. ACM, 2018,61(7):95−102.
[17] Koblitz N. Elliptic curve cryptosystems. Mathematics of Computation, 1987,48:203−209.
[18] Gu ZL, Zheng SH, Yang YX. Modern Cryptography. 2nd ed., Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press,
2015. 190−207 (in Chinese).